介绍
FilamentWinding用于计算纤维缠绕路径,预测纤维缠绕厚度。
原理
简介
纤维缠绕是一种比较成熟的工艺,如下图所示,旋转芯模以角速度 ω 旋转,丝束头从树脂槽中蘸取树脂,纤维带在张力 F 作用下,按一定角度 φ、宽度 w 铺覆到芯模上;移动平台以速度 v 带动丝束头等移动,实现纤维带在芯模不同位置的缠绕 。通常可用于制造筒状构件、压力容器、火箭发动机壳体、发动机整流罩等。
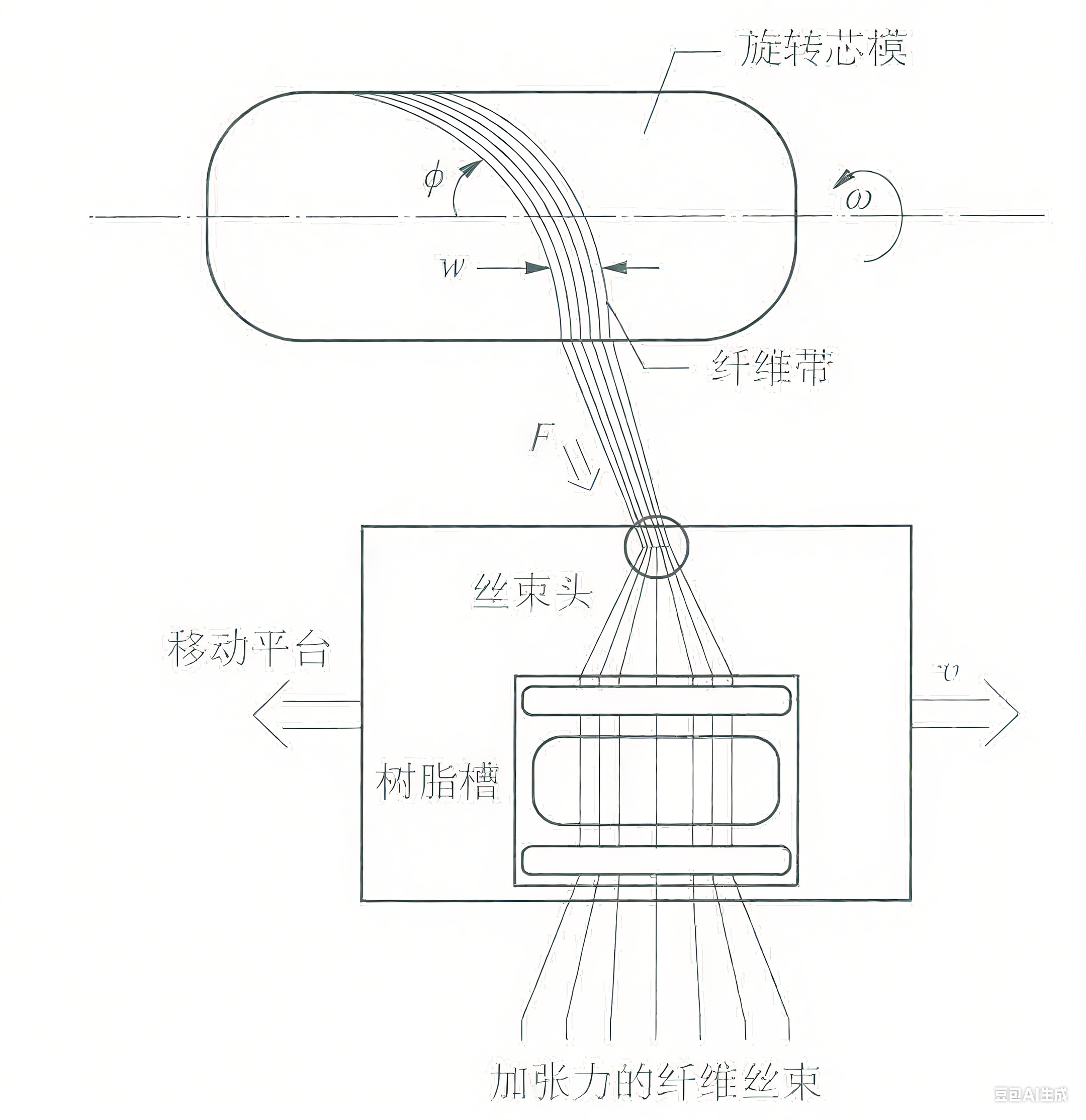
测地线缠绕
There are other interesting properties of axisymmetric bodies, as discovered by the prominent French mathematician Alexis Claude de Clairault. Clairault’s relation is a formula in classical differential geometry. The relation is valid for any point on a geodesic path on an arbitrary surface of revolution and gives:
$$
rsin(\phi)=constant
$$
where r is the radial distance of any point on a geodesic path from the axis of revolution, and A is the angle between the tangent vector and the latitudinal circle, or, to nonmathematicians, A is the winding angle.
非测地线缠绕
对于一般曲面的缠绕角方程如下:
$$
\frac{d\alpha}{dx}=\frac{|\lambda[-r(x)r’’(x)cos^2 \alpha+[1+r’^2(x)sin^2\alpha]]-[1+r’^2(x)]r’(x)sin\alpha|}{[1+r’^2(x)]r(x)cos(\alpha)}
$$
式中,$\alpha$为缠绕角,$\lambda$为摩擦系数,x为长度,r为半径。
通过求解上式可计算非测地线的缠绕路径。
纤维厚度预测
缠绕模型任意平行圆处的纤维厚度为:
$$
t_f=\frac{Rcos\alpha_0}{rcos\alpha}t_{f\alpha}
$$
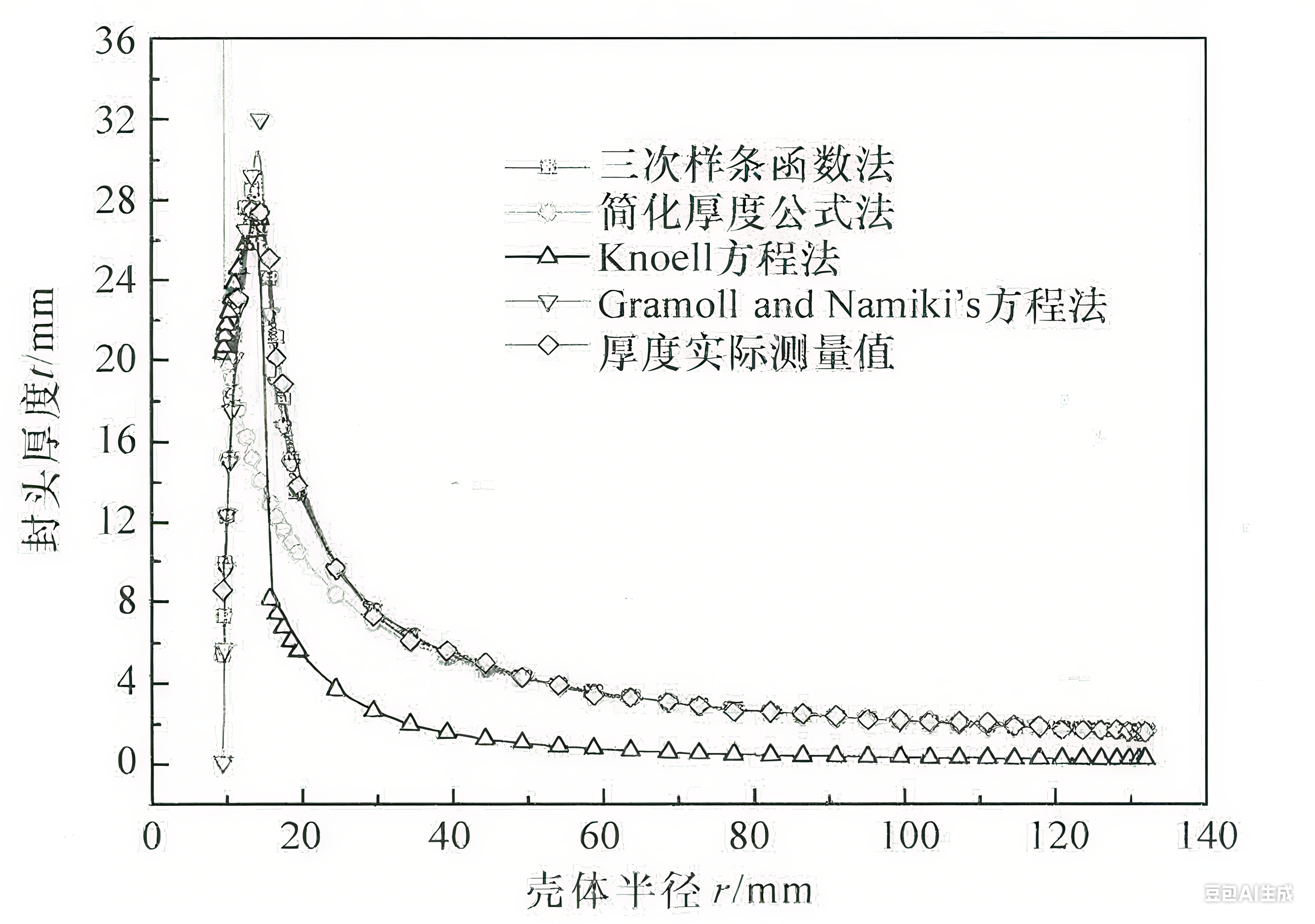
该公式可以预测任意平面的厚度,但当$\alpha$为90对时,分母为0,厚度会无限大,需对边缘处的厚度进行调整。
在封头处约1个带宽长度处会出现厚度峰值,可采用不同的方式来平滑曲线,以下列举了几种不同的方法:
类结构
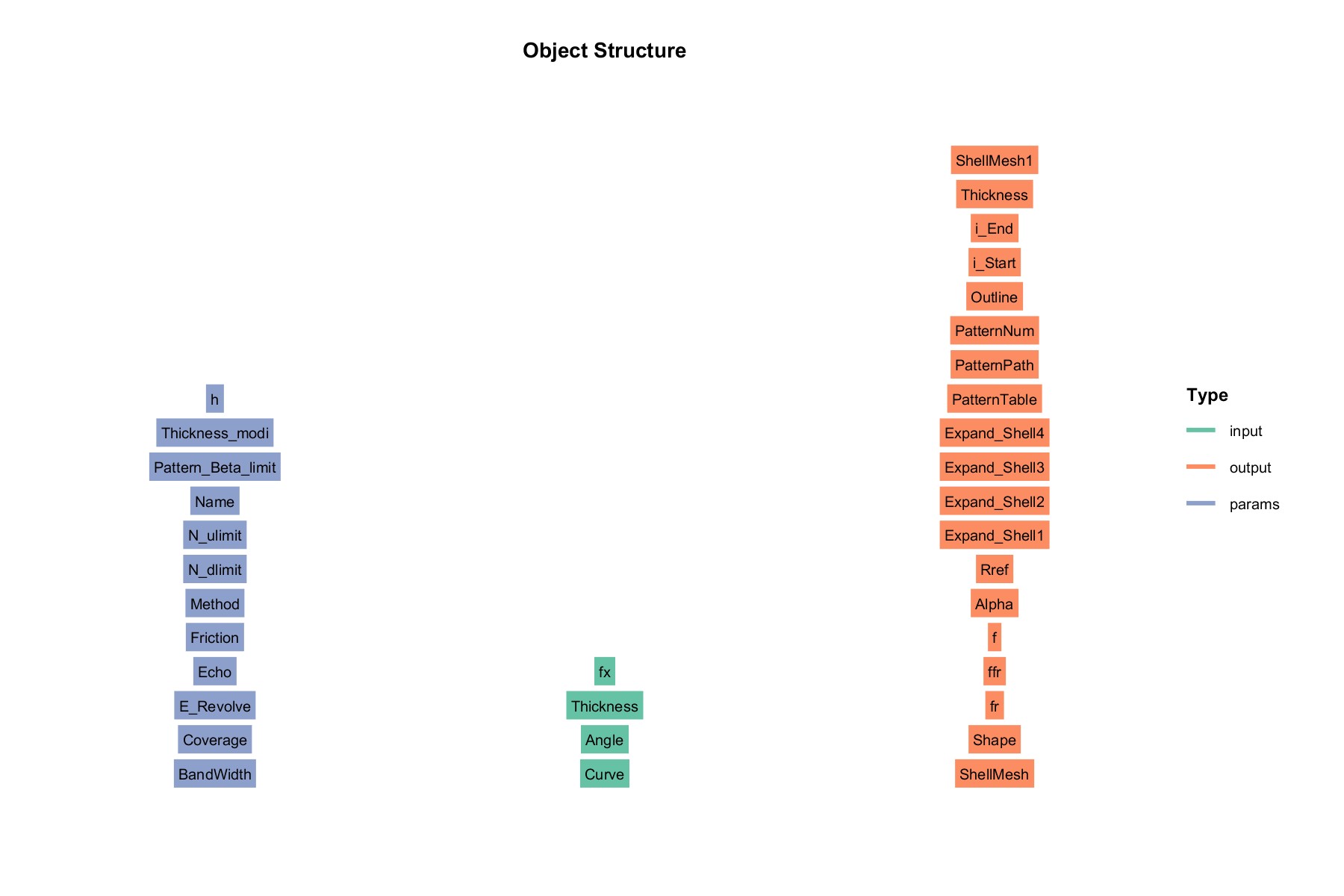
输入 input:
- Thickness : 缠绕厚度
- Angle : 缠绕角度
- Curve : 芯模曲线
参数 params:
- h : 迭代步长
- Thickness_modi : 厚度修正因子
- Pattern_Beta_limit : 线型角度限制参数
- Name : 名称
- N_ulimit :N上偏差
- N_dlimit :N下偏差
- Method : 缠绕方法
- Friction : 两端摩擦系数
- E_Revolve :网格旋转次数
- Coverage : 覆盖率
- BandWidth : 纤维带宽
输出 output :
- ShellMesh1 : 外轮廓网格
- Thickness : 厚度分布
- i_End : 缠绕终止处
- i_Start : 缠绕起始处
- Outline : 外轮廓
- PatternNum : 线型编号
- PatternPath :缠绕路径
- PatternTable : 线型选型表
- Expand_Shell1 : 展开图1
- Expand_Shell2 : 展开图2
- Expand_Shell3 : 展开图3
- Expand_Shell4 : 展开图4
- Rref : 参考半径
- Alpha : 缠绕角度
- f : 摩擦系数
- ffr : 二阶导数
- fr : 一阶导数
- Shape : 形状
- ShellMesh : 内轮廓网格
案例
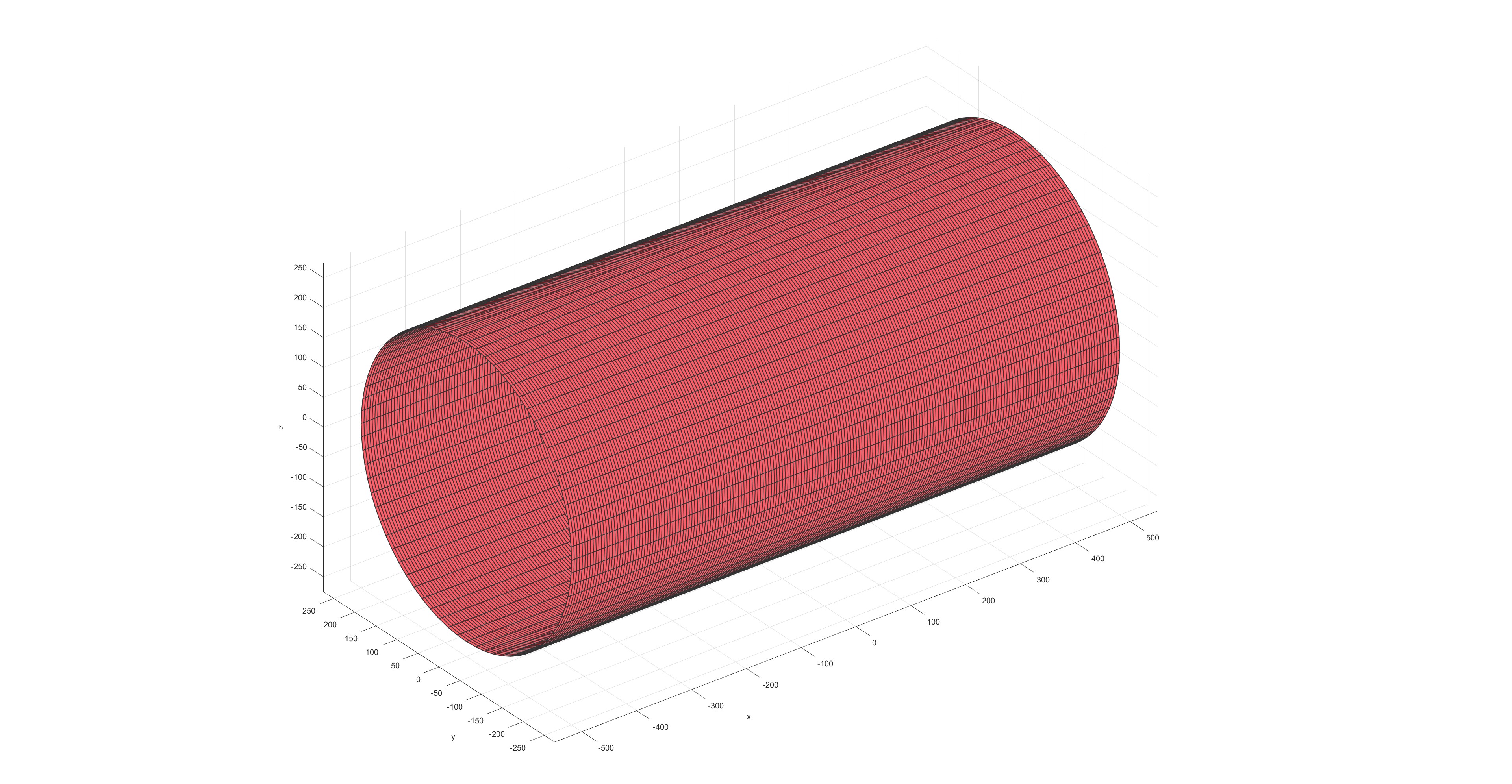
Cylinder winding (Flag=1)
inputStruct1.Curve=[(-500:5:500)',ones(201,1)*250];
inputStruct1.Angle=60;
inputStruct1.Thickness=2.5;
paramsStruct1.Method=1;
paramsStruct1.Friction=[0.1,0.1];
M= solve.FilamentWinding(paramsStruct1, inputStruct1);
M= M.solve();
PlotShellMesh(M);
PlotExpandShell(M);
PlotPath(M);
PlotPath(M,'pattern',2);
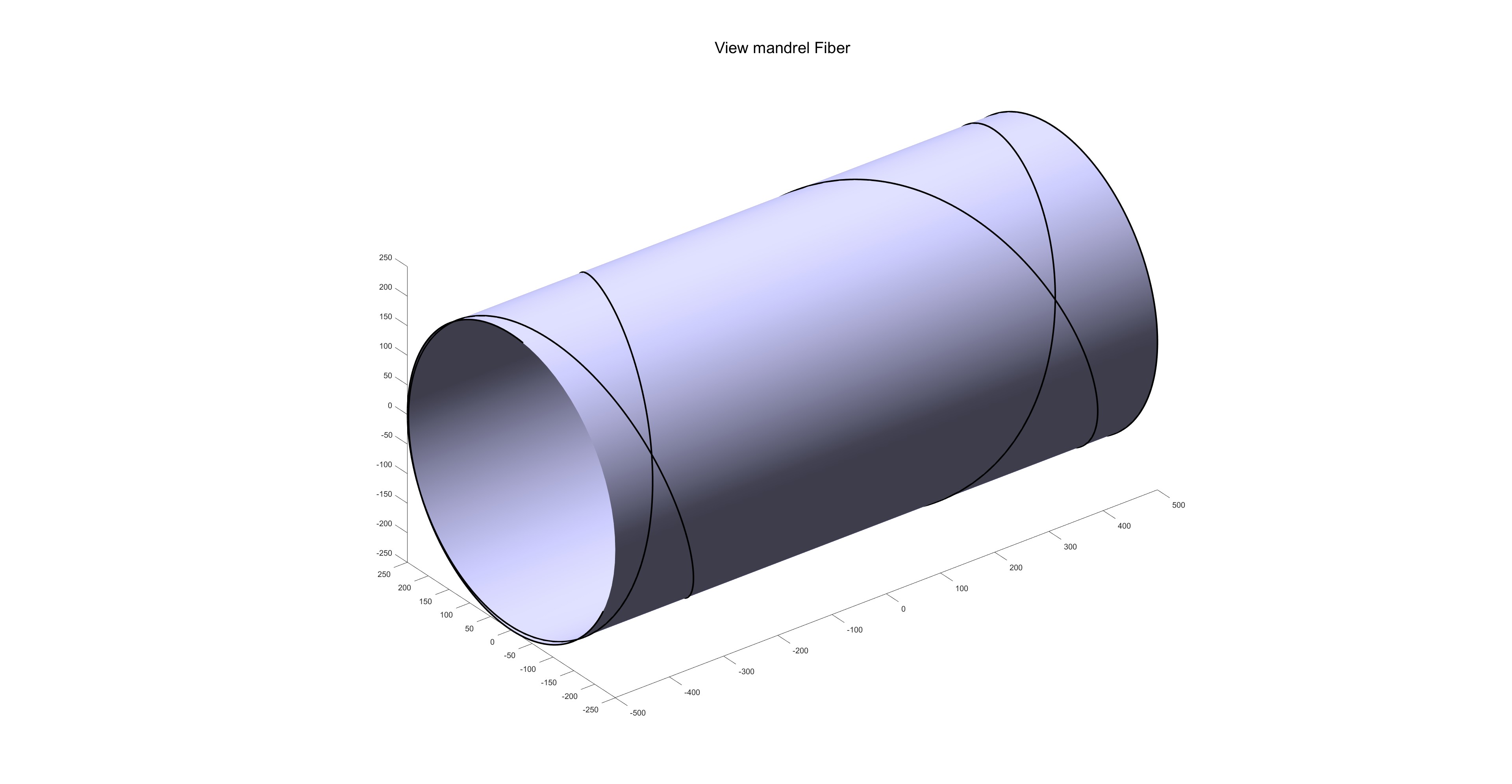
圆柱芯模:
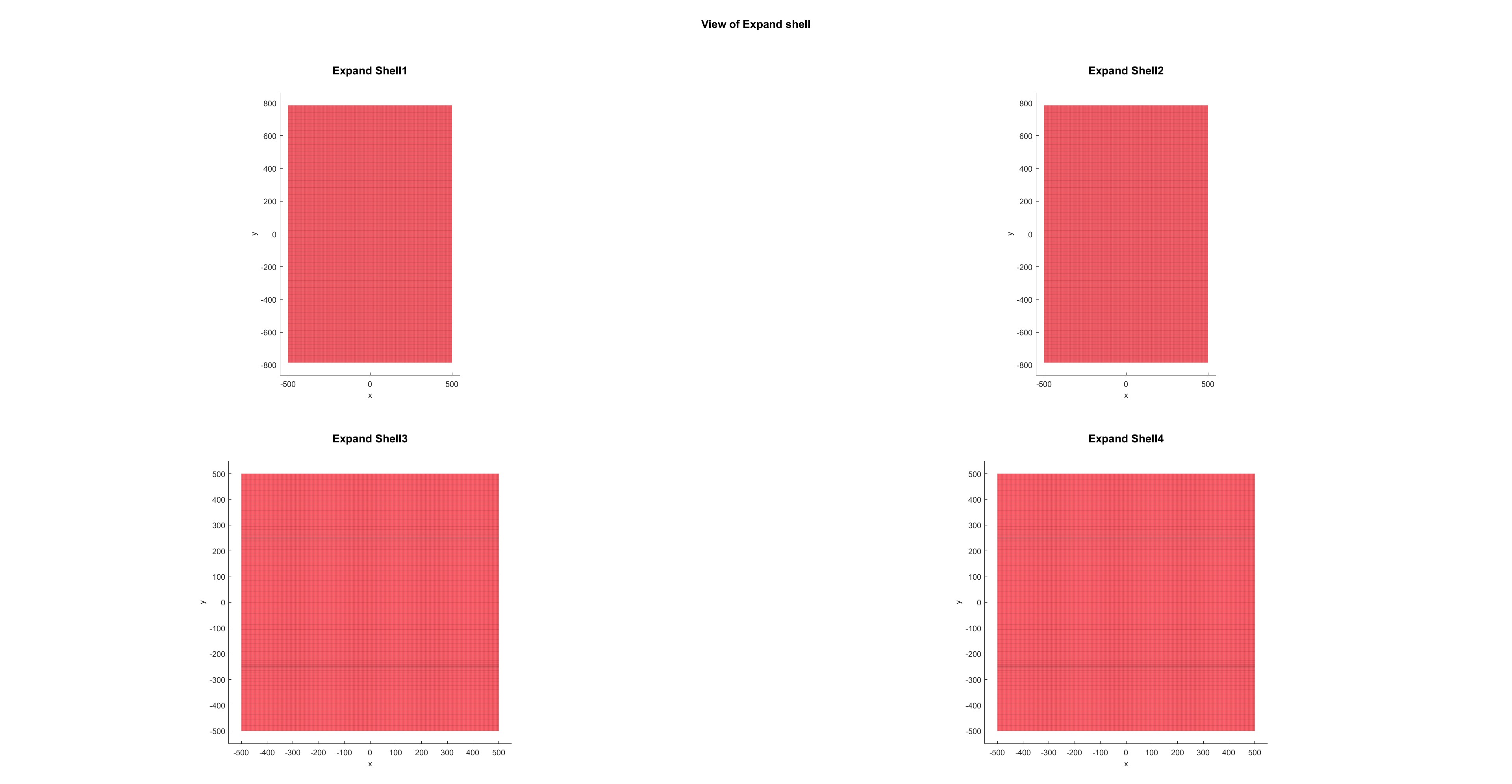
不同投影的展开图:
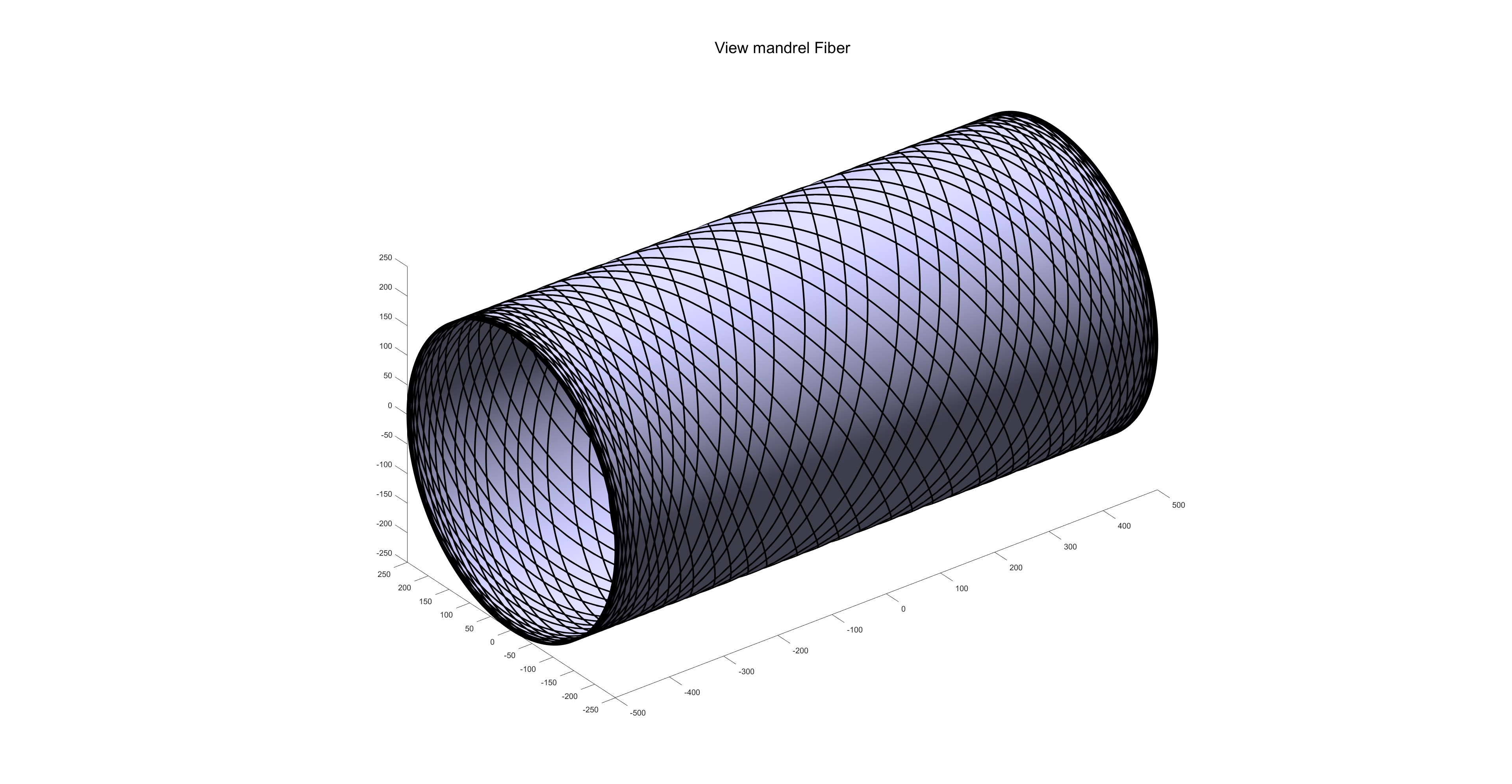
缠绕路径:
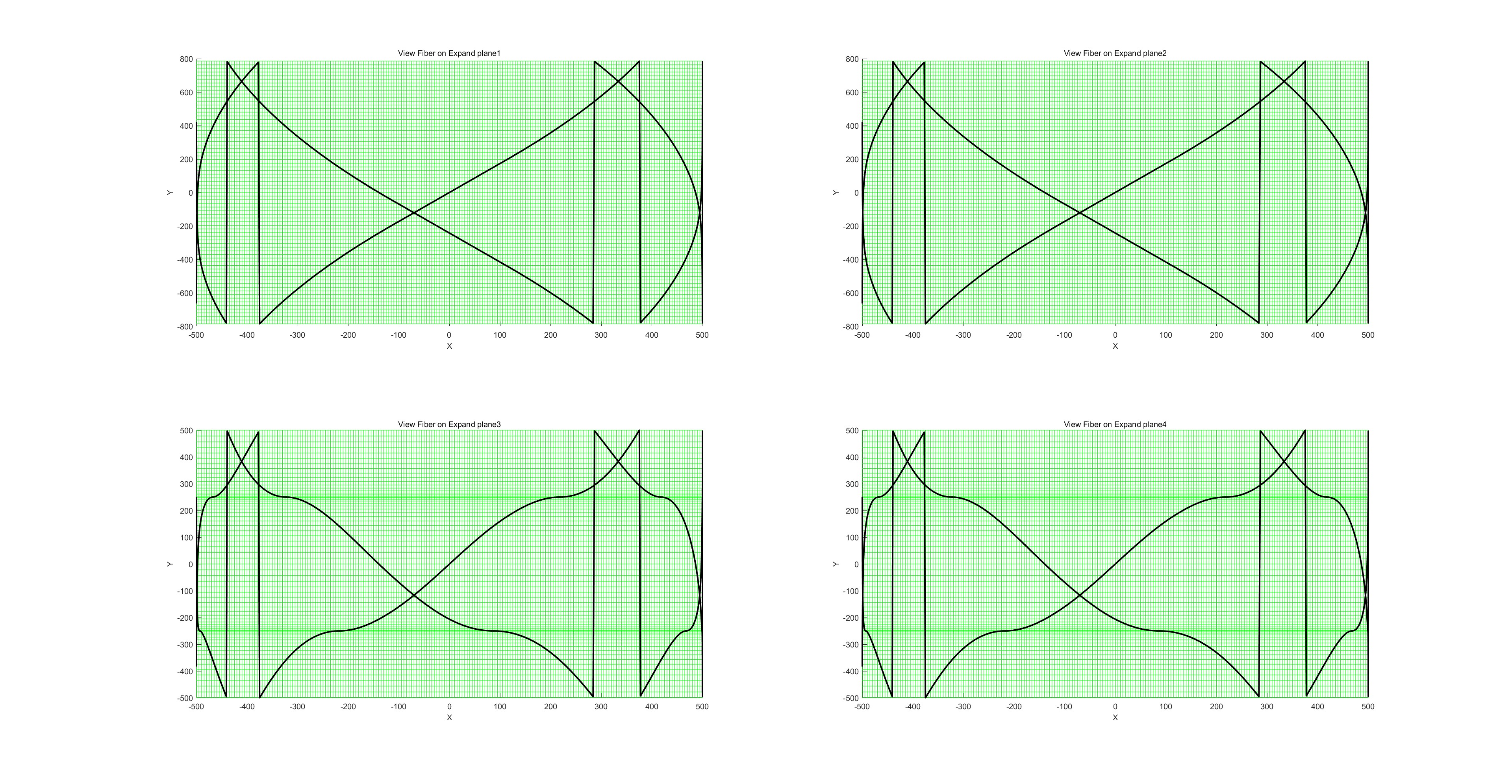
路径投影:
缠绕线型:
Pressure vessel winding (Flag=2)
a=Point2D('Point','Echo',0);
b=Line2D('Line','Echo',0);
a=AddPoint(a,-100,0);
a=AddPoint(a,[-100;100],[360;360]);
a=AddPoint(a,100,0);
b=AddCircle(b,360,a,1,'sang',160,'ang',-70,'seg',400);
b=AddLine(b,a,2);
b=AddCircle(b,360,a,3,'sang',90,'ang',-70,'seg',400);
x=b.Point.P(:,1);
y=b.Point.P(:,2);
gap=(max(x)-min(x))/500;
xx=min(x):gap:max(x);
yy=interp1(x,y,xx,'spline');
inputStruct1.Curve=[xx',yy'];
inputStruct1.Angle=60;
% inputStruct1.Angle=21;
inputStruct1.Thickness=2.5;
% paramsStruct1.Method=1;
paramsStruct1.Method=2;
paramsStruct1.Friction=[0.1,0.1];
M= solve.FilamentWinding(paramsStruct1, inputStruct1);
M= M.solve();
PlotShellMesh(M);
PlotExpandShell(M);
PlotPath(M);
PlotPath(M,'pattern',2);
PlotFriction(M);
PlotThickness(M);
PlotAlpha(M);
PlotInnerLine(M);
PlotOuterLine(M);
PlotShape(M);
PlotShellMesh1(M);
压力容器芯模:
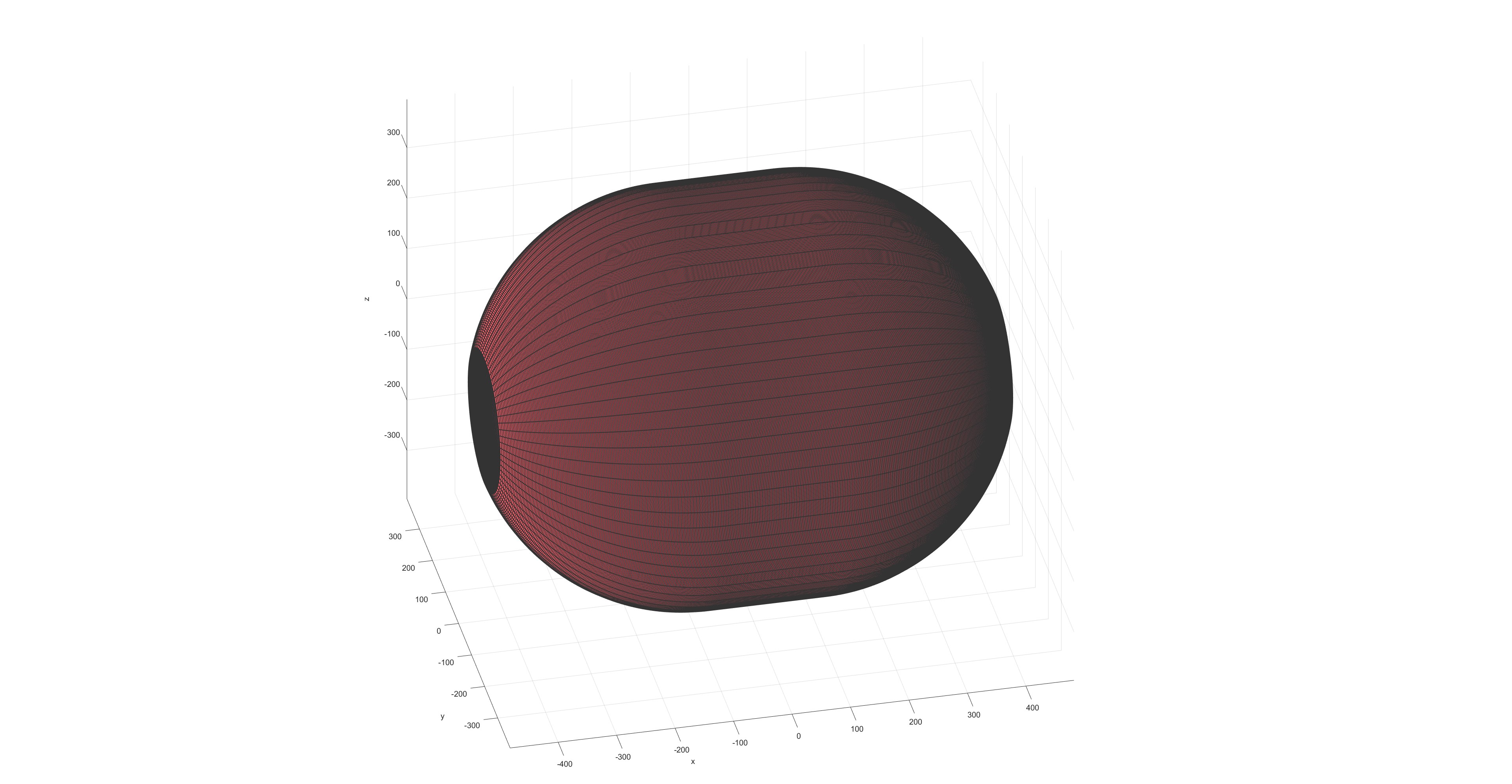
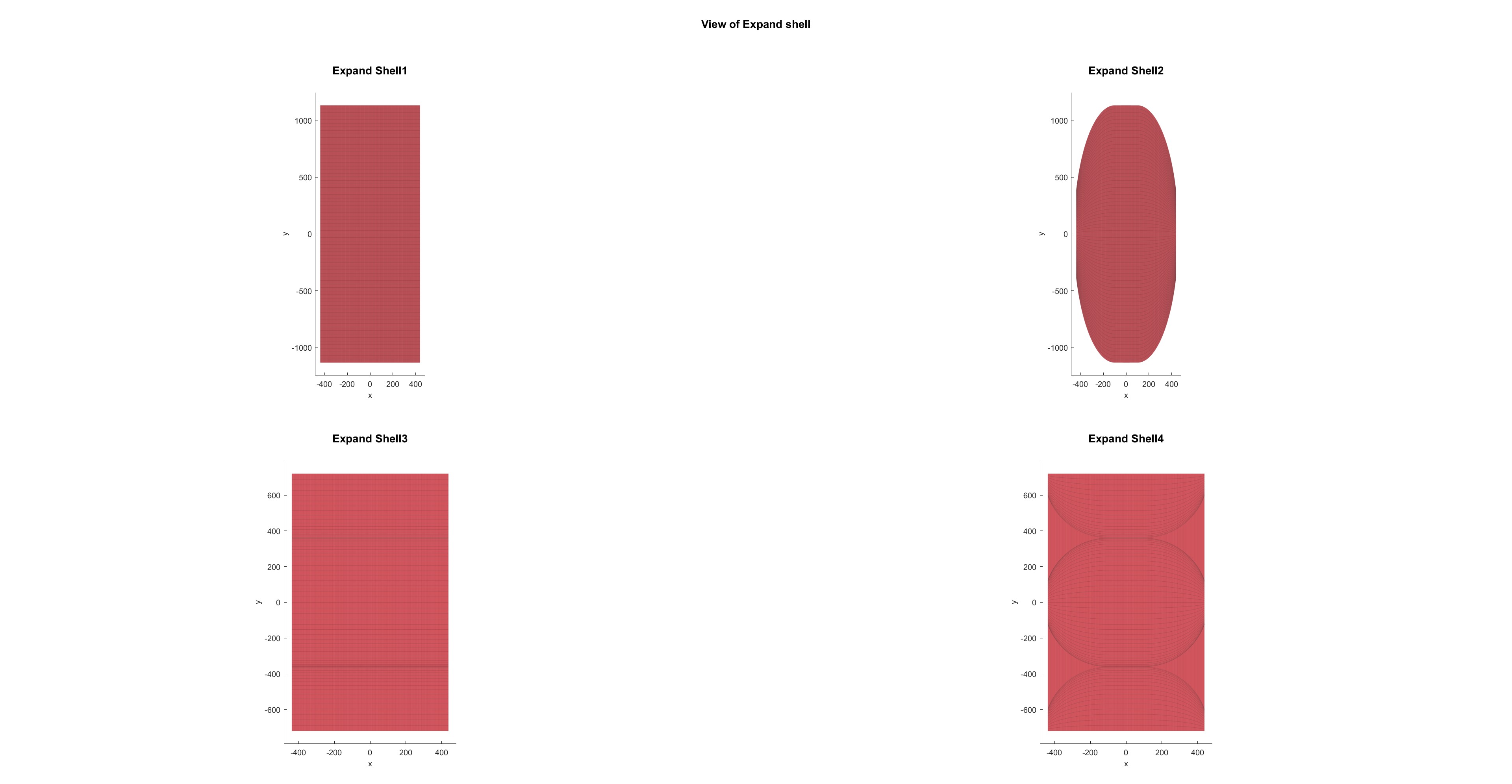
展开图:
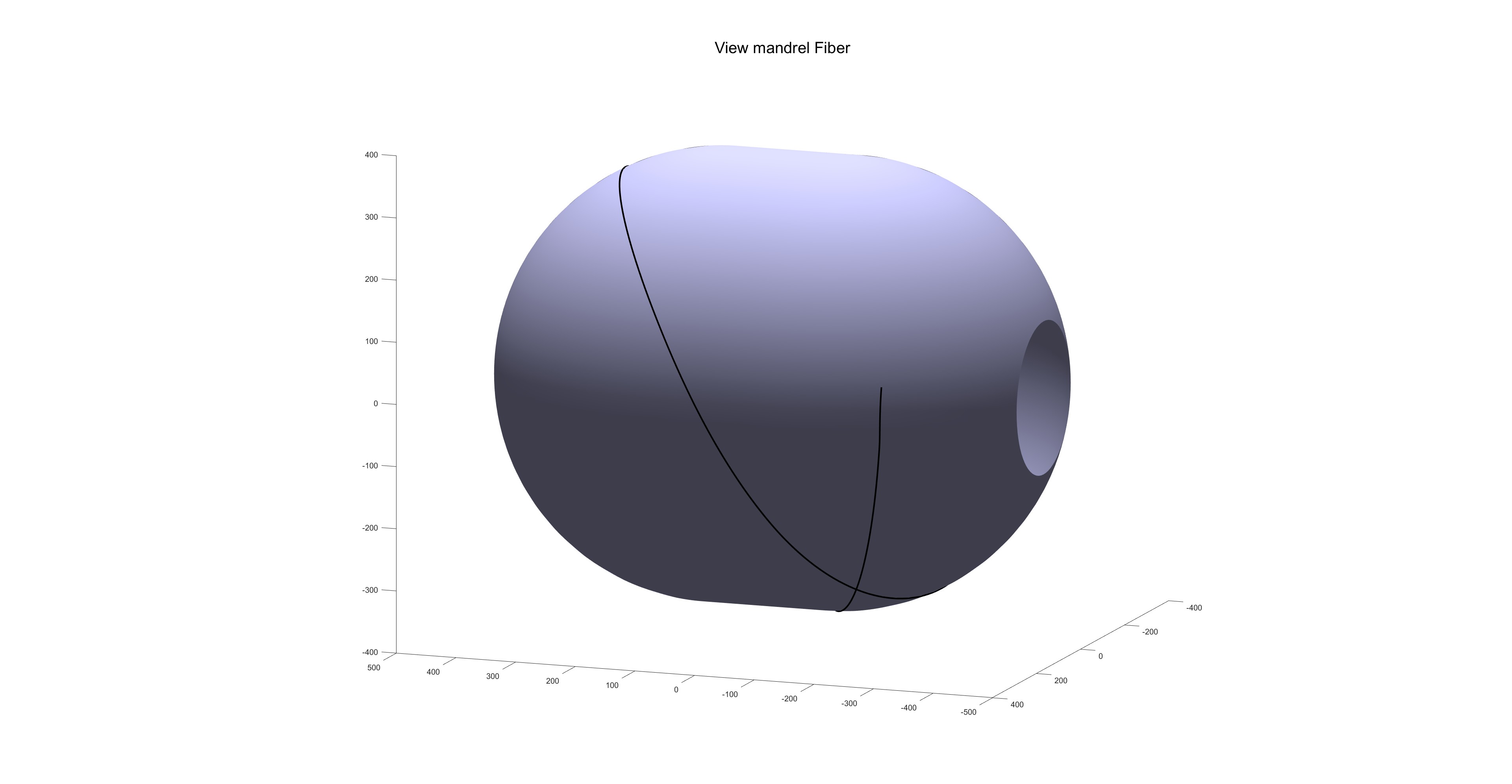
缠绕路径:
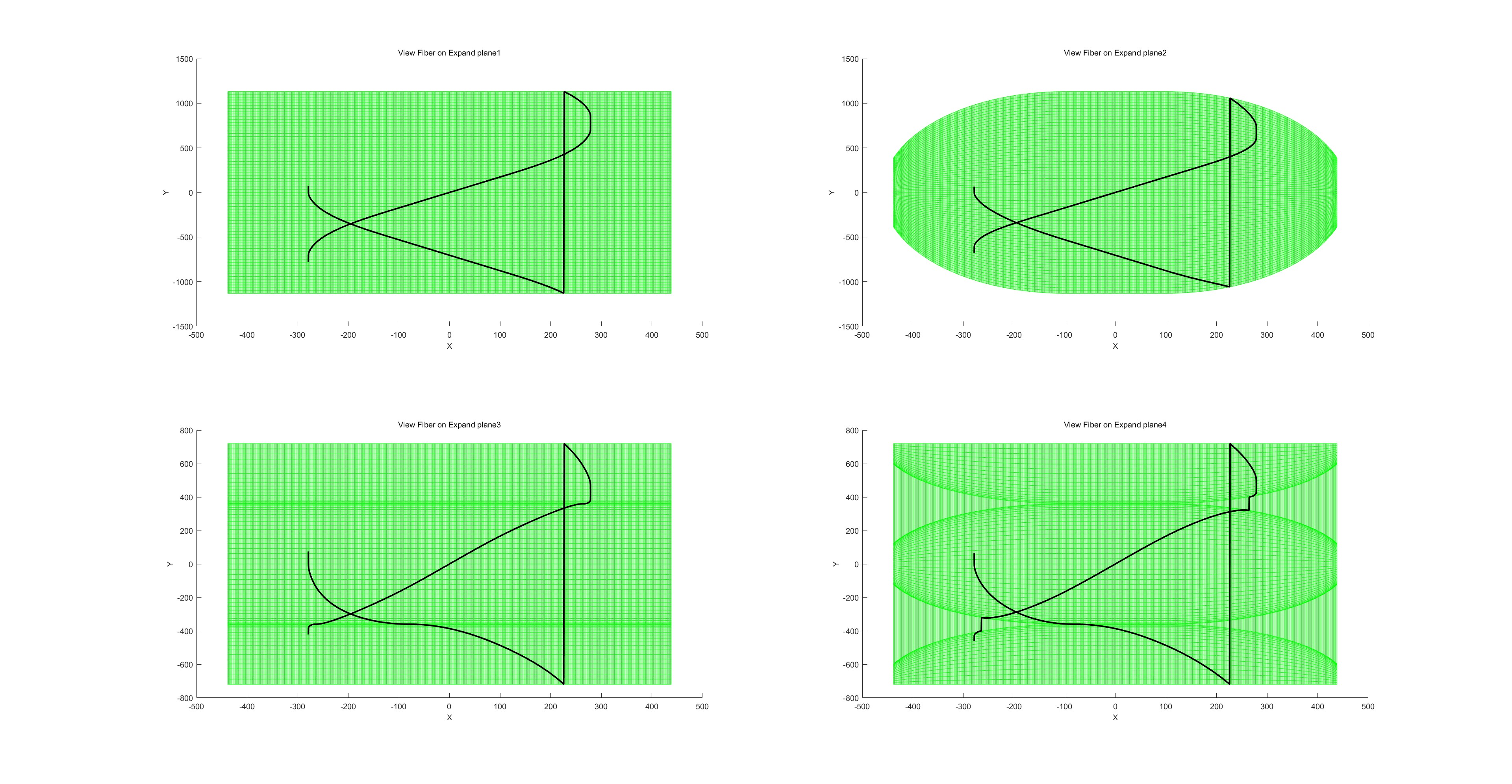
路径投影图:
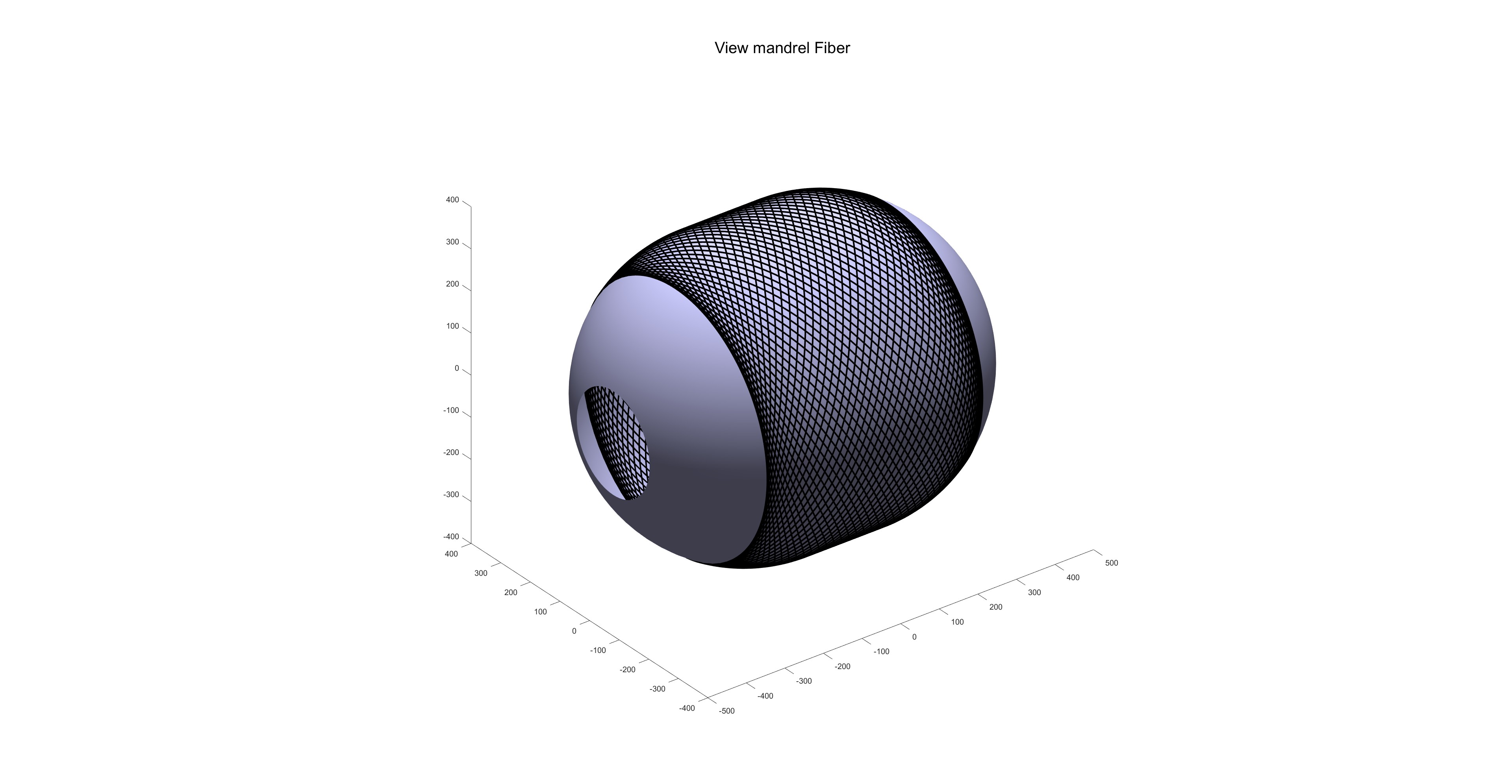
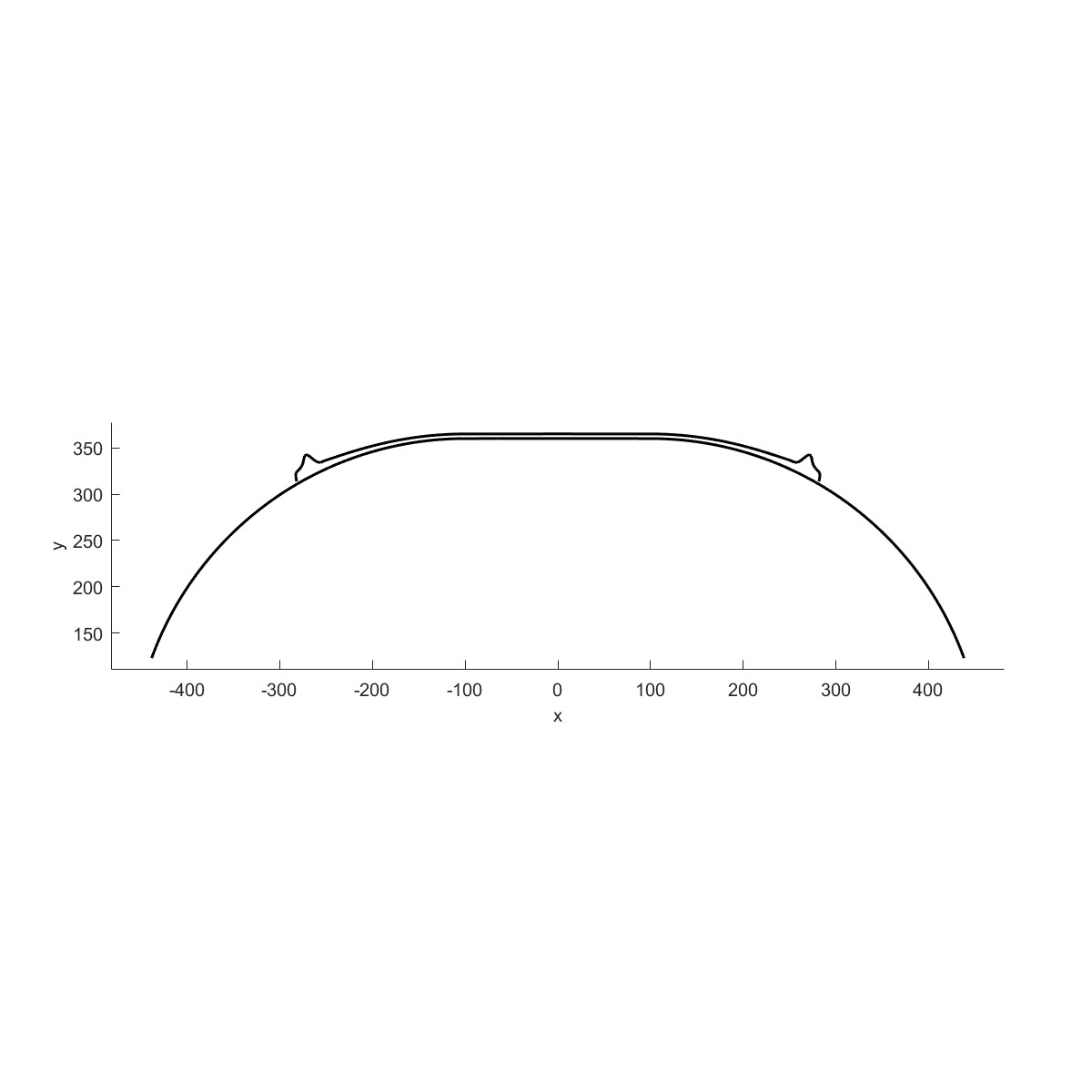
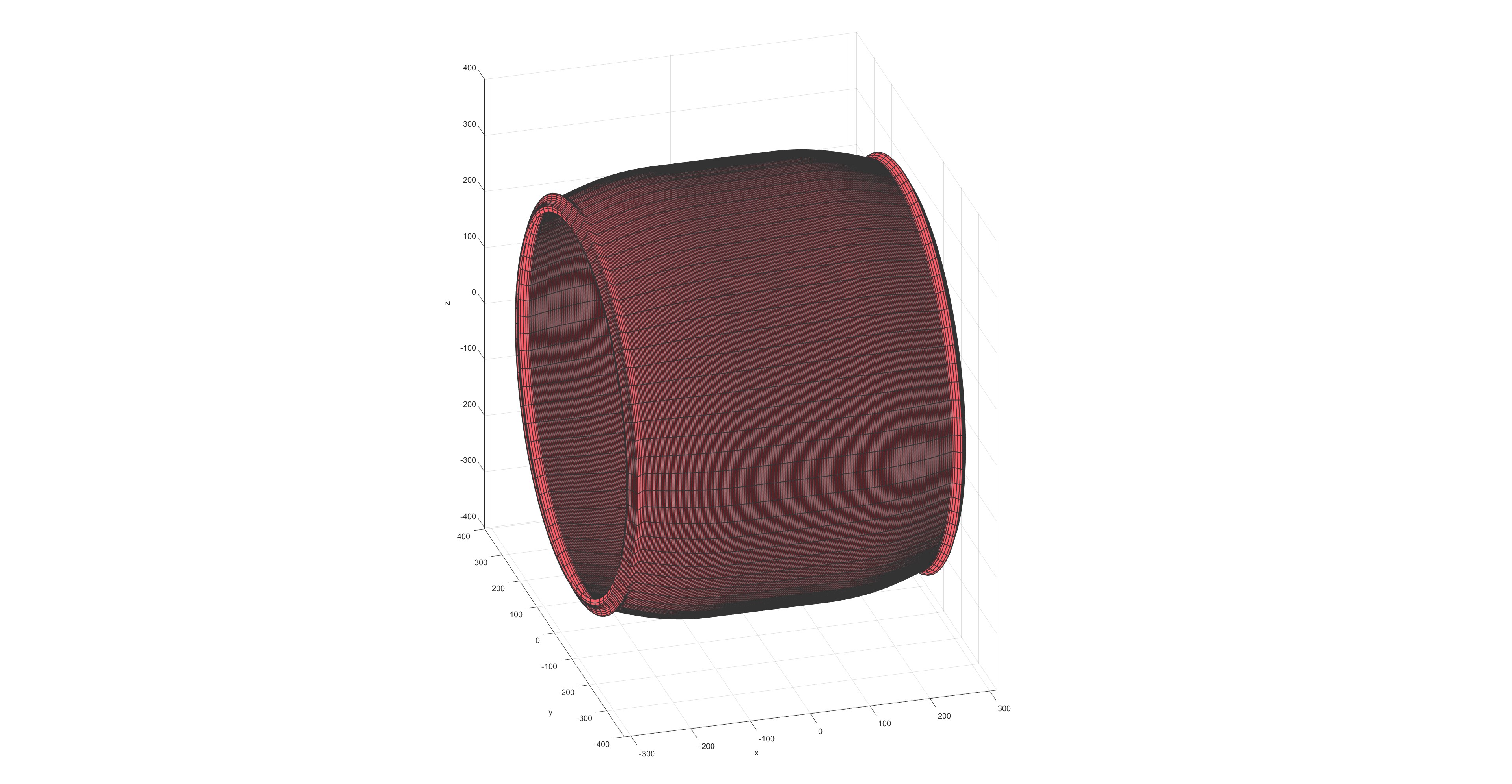
 缠绕完成后的效果图:
缠绕完成后的效果图:
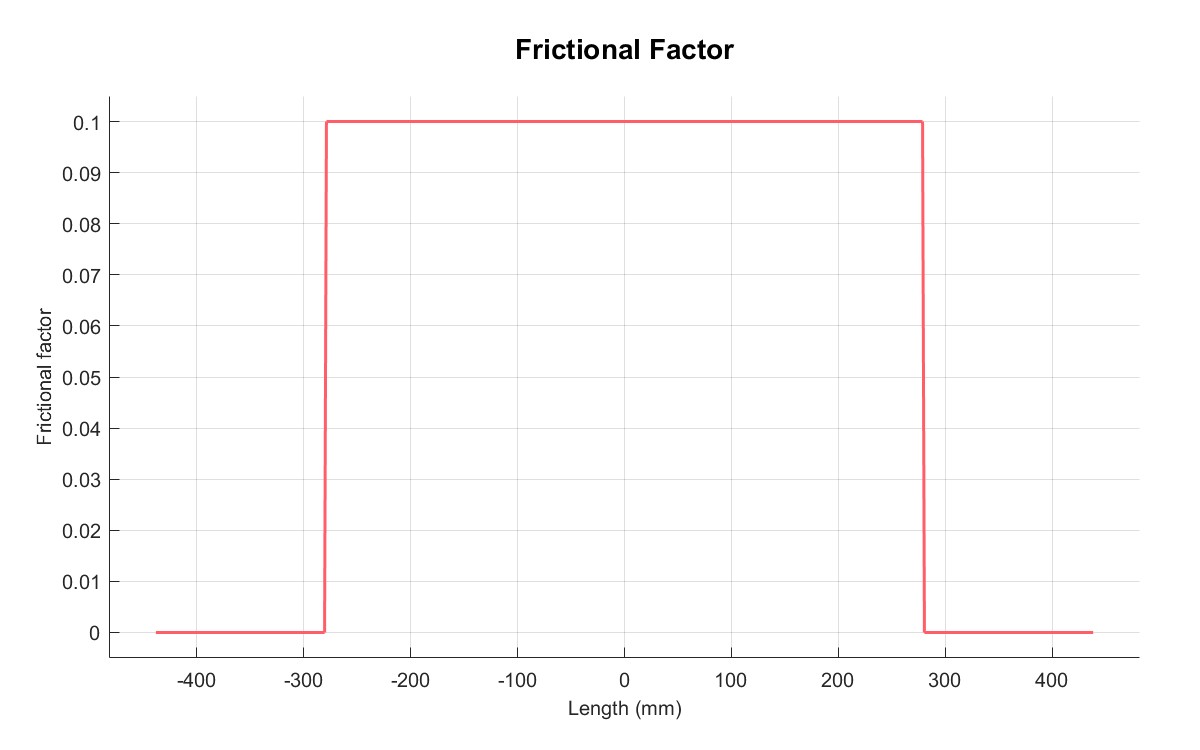 | 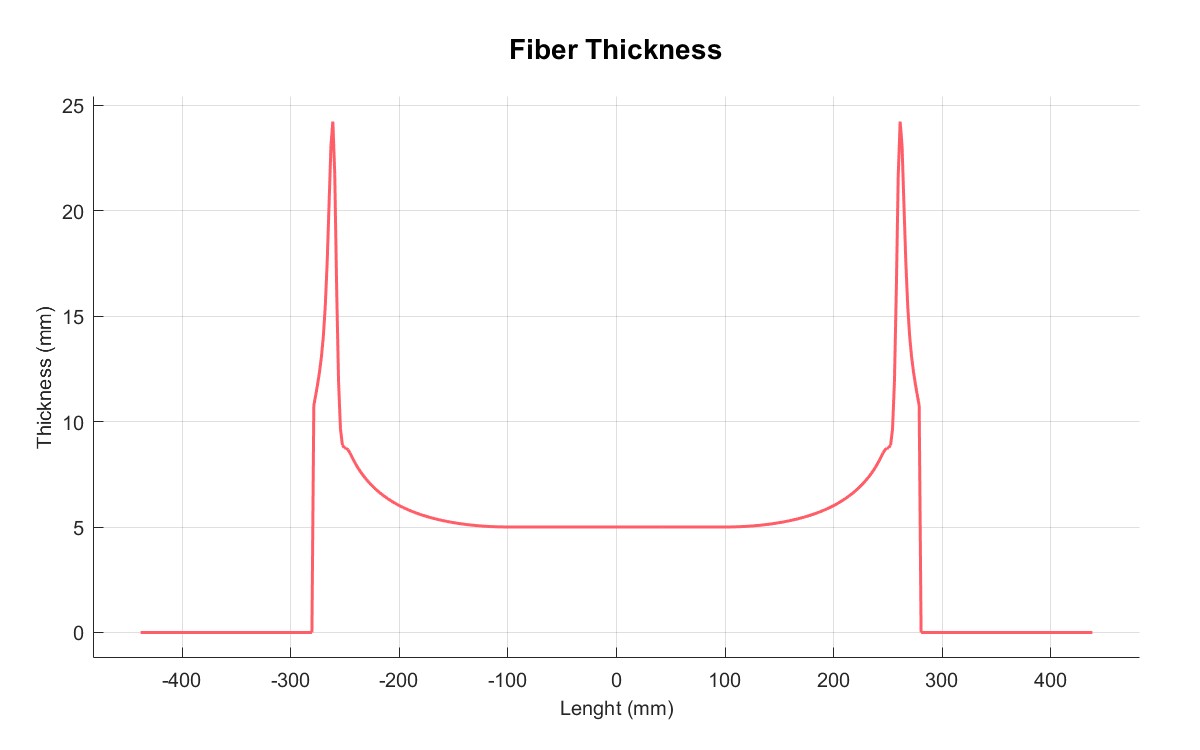 |
| 摩擦系数 | 厚度 |
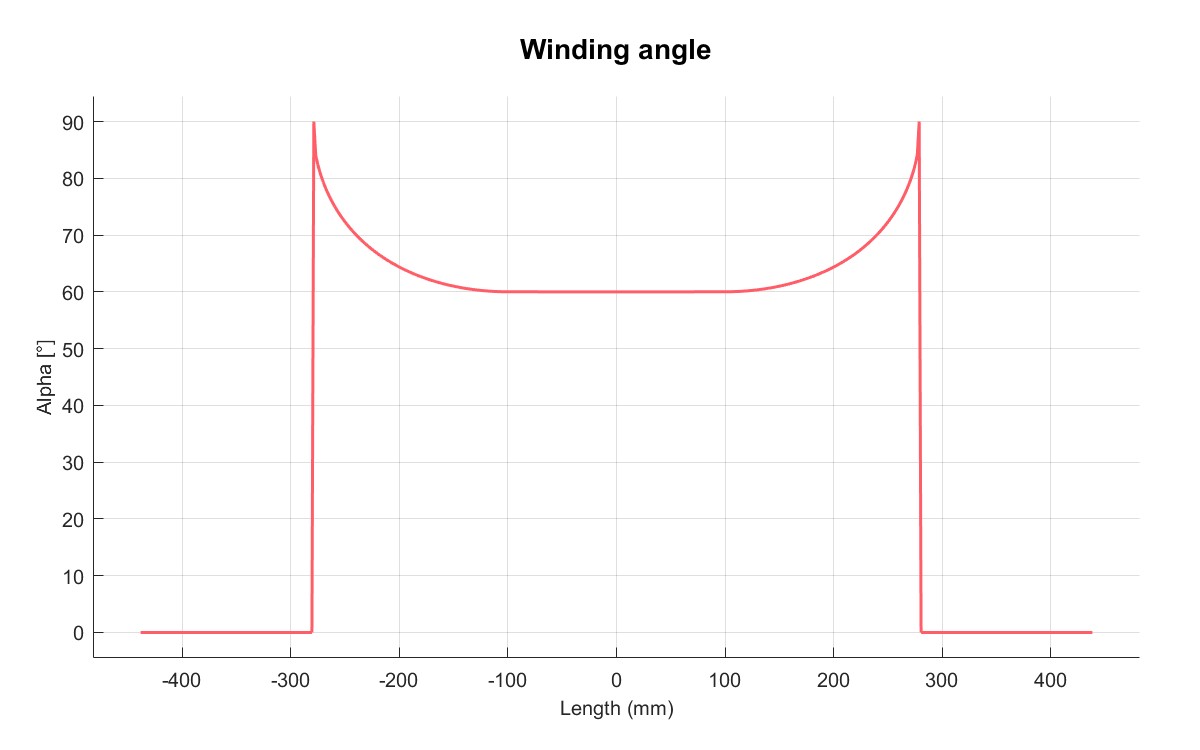 | 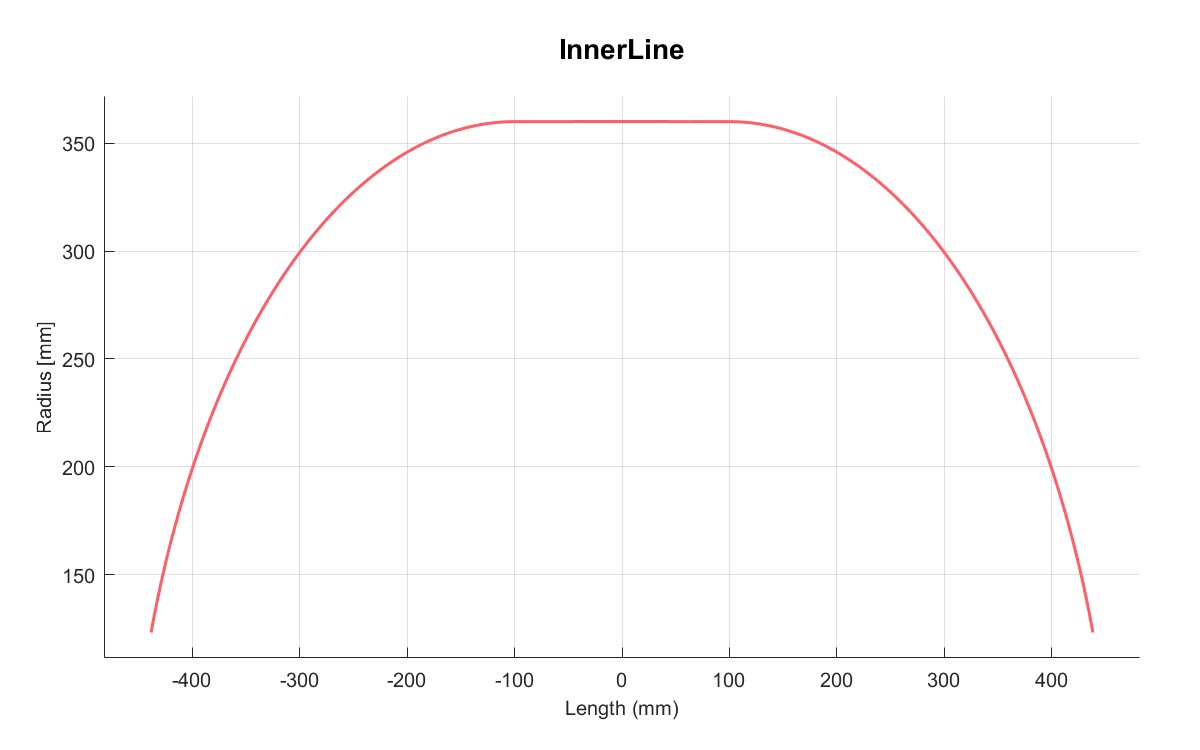 |
| 缠绕角度 | 内部轮廓线 |
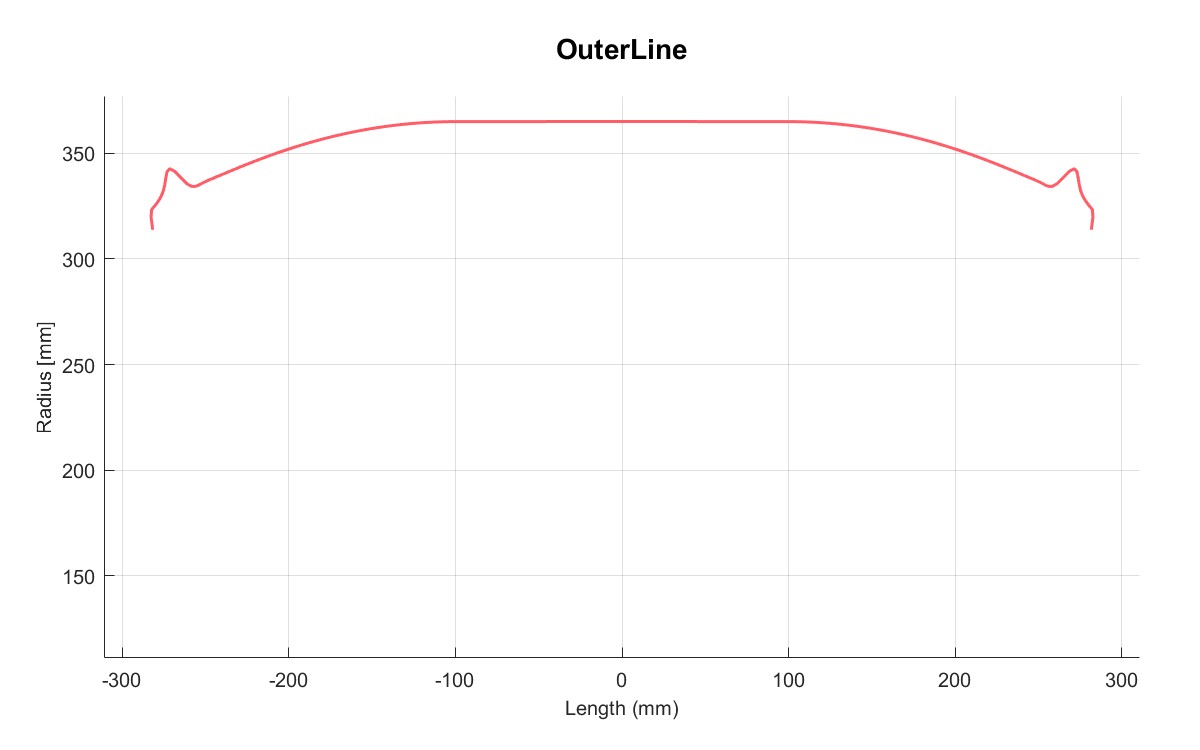 |  |
| 外部轮廓线 | 总轮廓线 |
Ellipse arch curve winding (Flag=3)
a=Point2D('Point','Echo',0);
b=Line2D('Line','Echo',0);
a=AddPoint(a,0,0);
b=AddEllipse(b,2500,600,a,1,'sang',160,'ang',-140);
x=b.Point.P(:,1);
y=b.Point.P(:,2);
gap=(max(x)-min(x))/500;
xx=min(x):gap:max(x);
yy=interp1(x,y,xx,'spline');
inputStruct1.Curve=[xx',yy'];
inputStruct1.Angle=35;
inputStruct1.Thickness=2.5;
paramsStruct1.Friction=[0.2,0.2];
paramsStruct1.Method=2;
M= solve.FilamentWinding(paramsStruct1, inputStruct1);
M= M.solve();
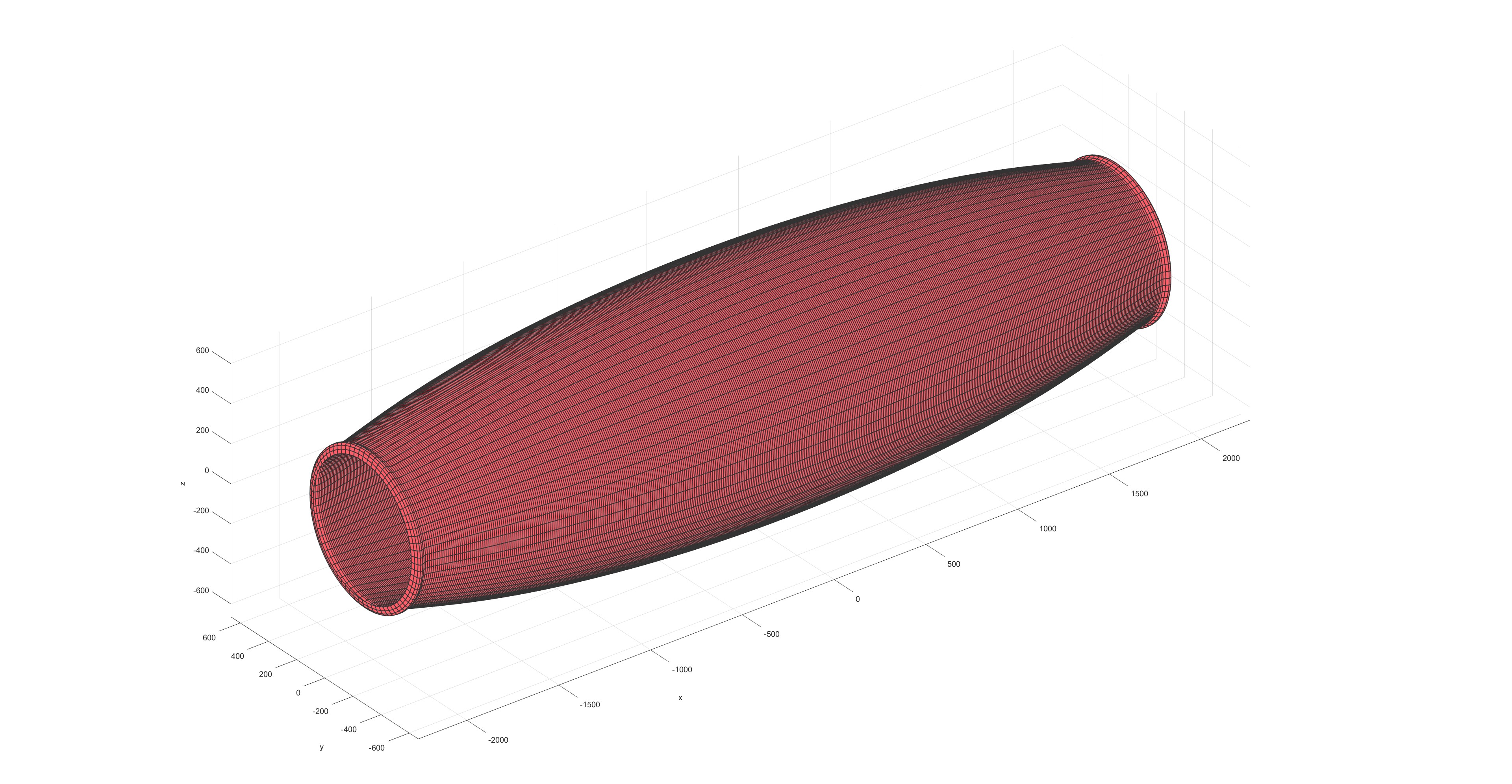
PlotShellMesh(M);
PlotExpandShell(M);
PlotPath(M);
PlotPath(M,'pattern',2);
PlotFriction(M);
PlotThickness(M);
PlotAlpha(M);
PlotInnerLine(M);
PlotOuterLine(M);
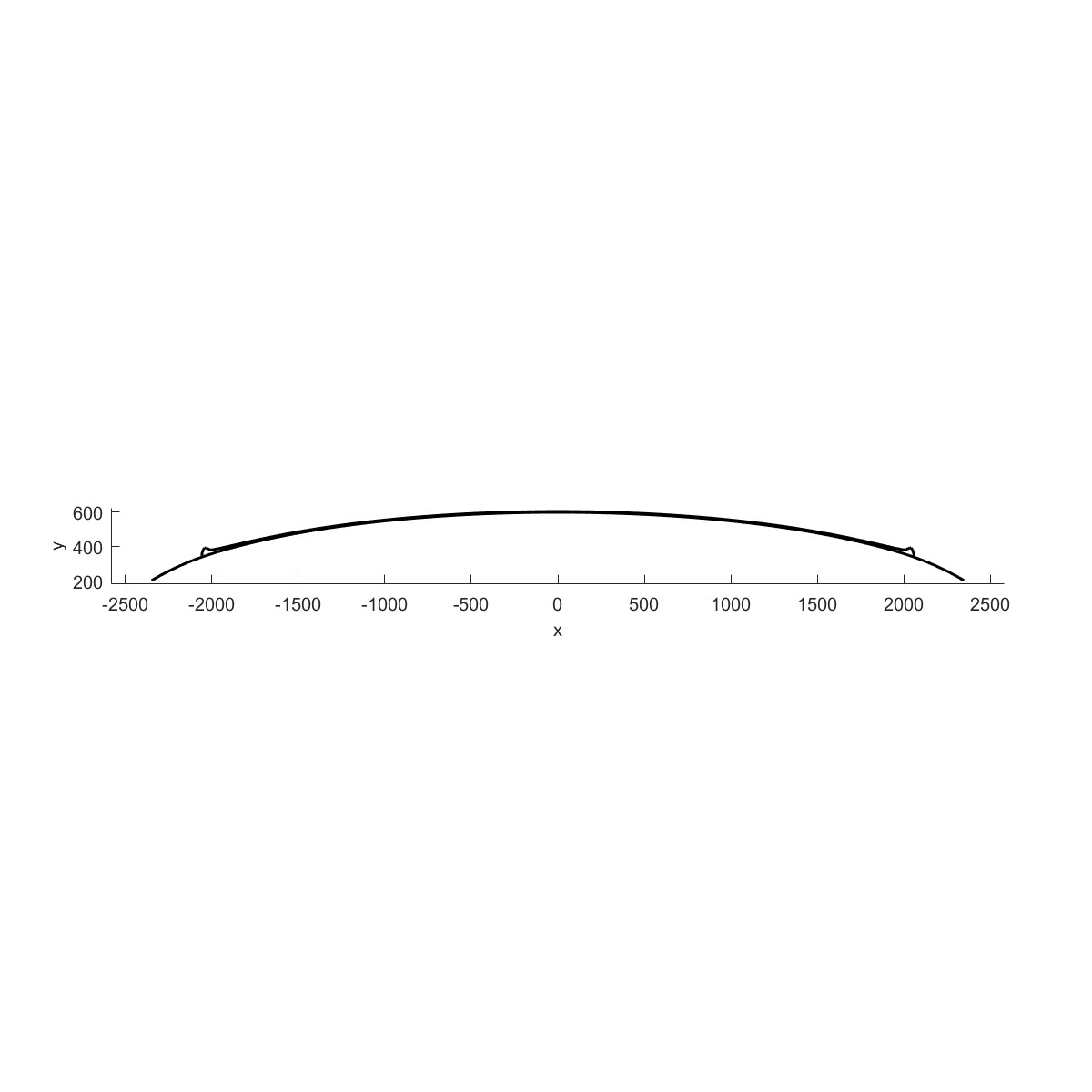
PlotShape(M);
PlotShellMesh1(M);
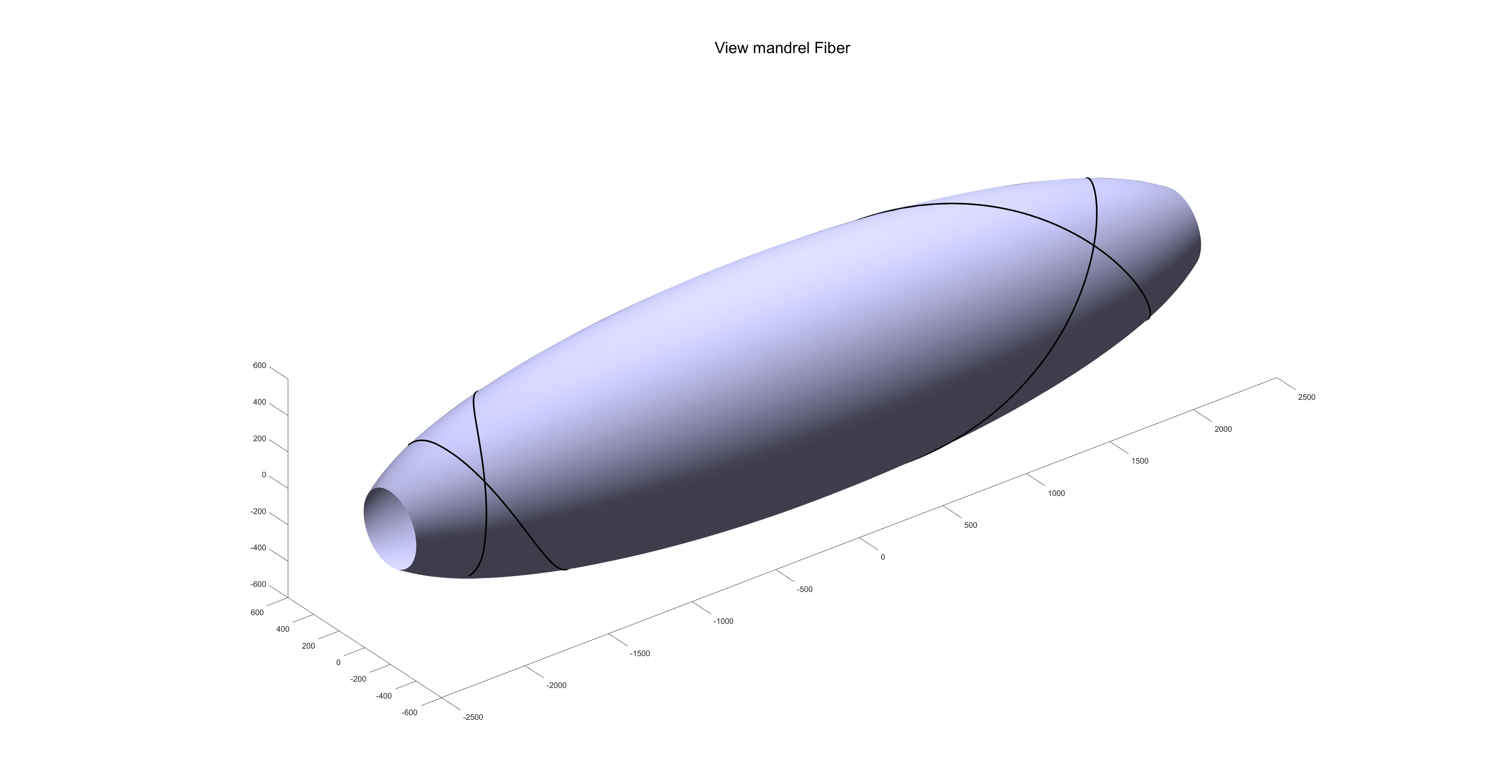
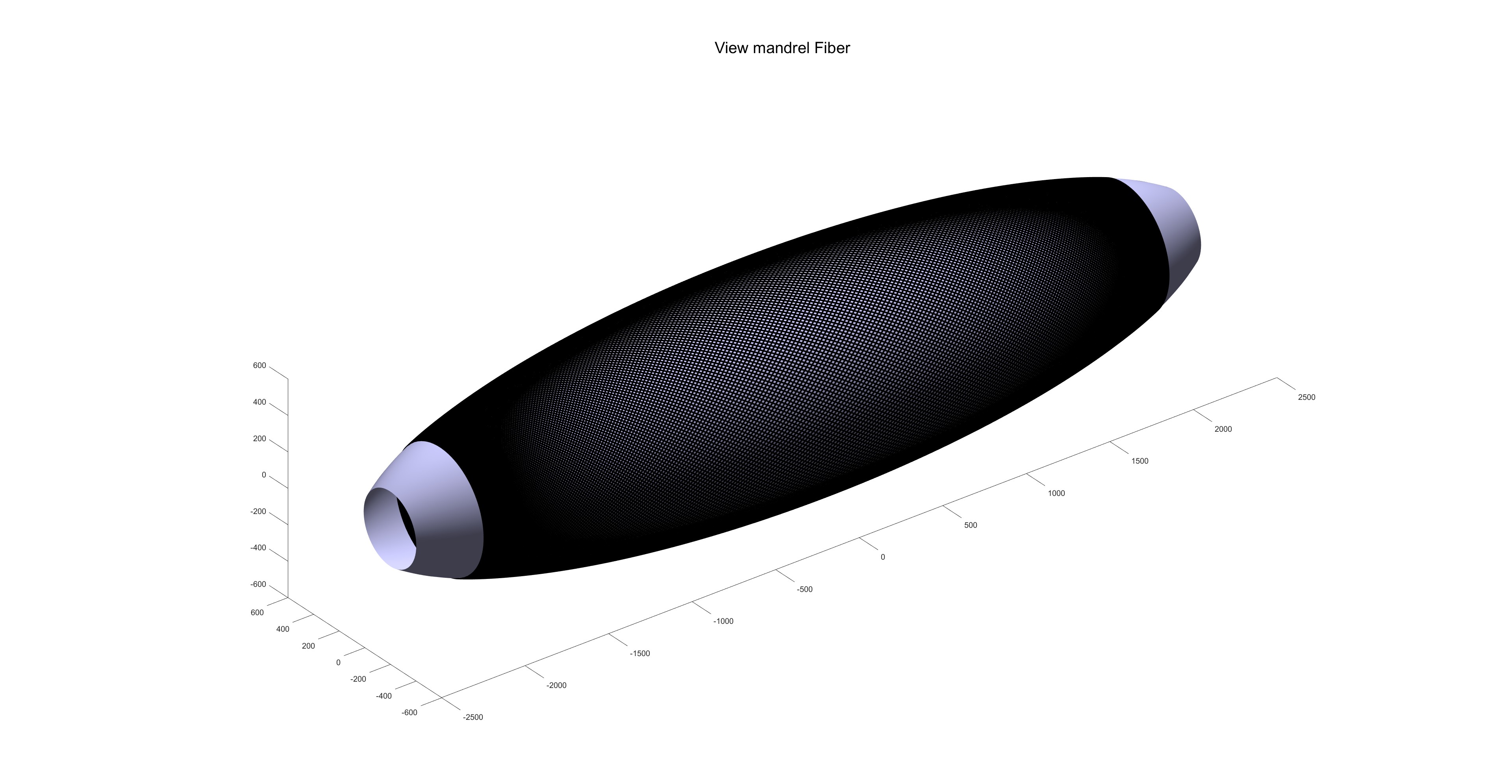
芯模形状:
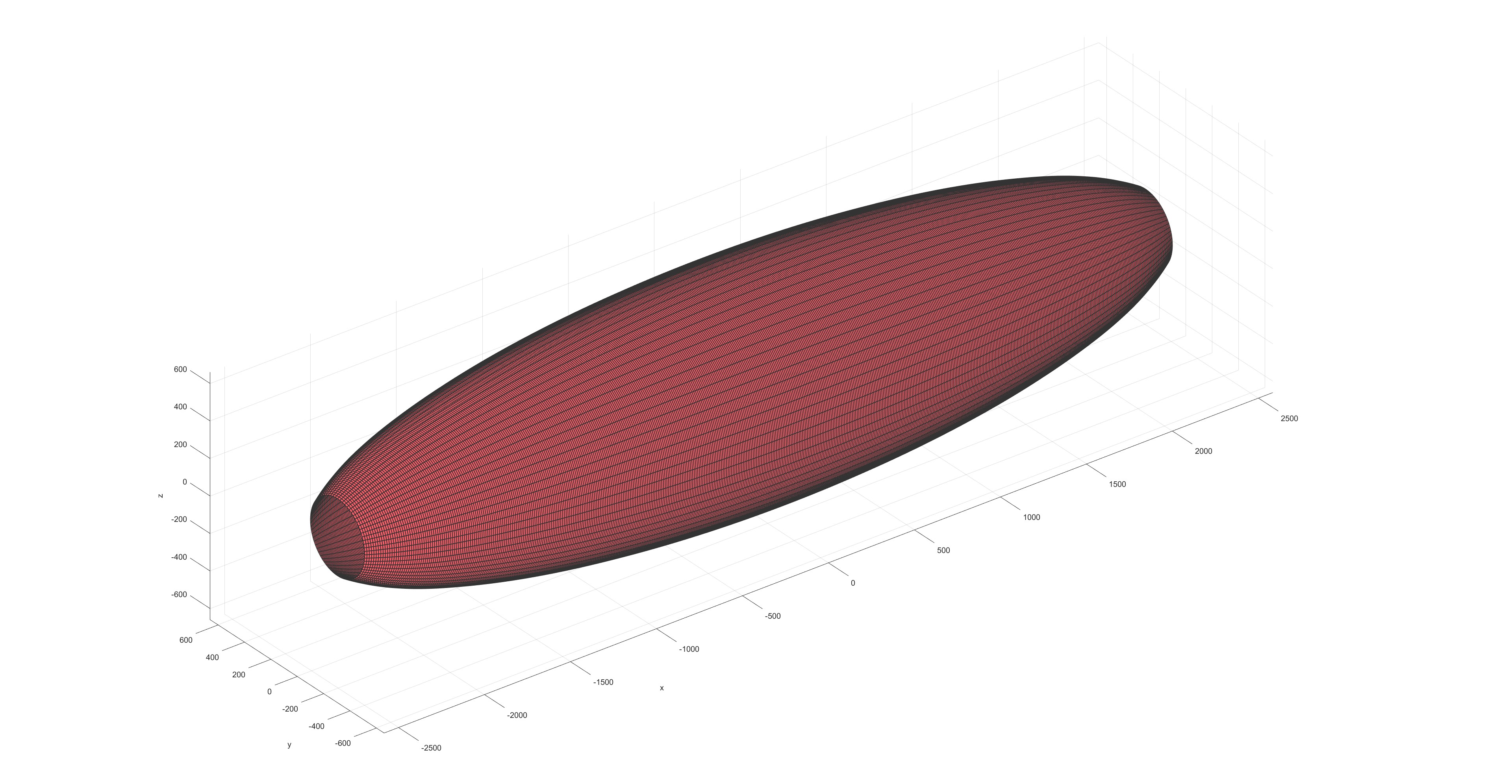
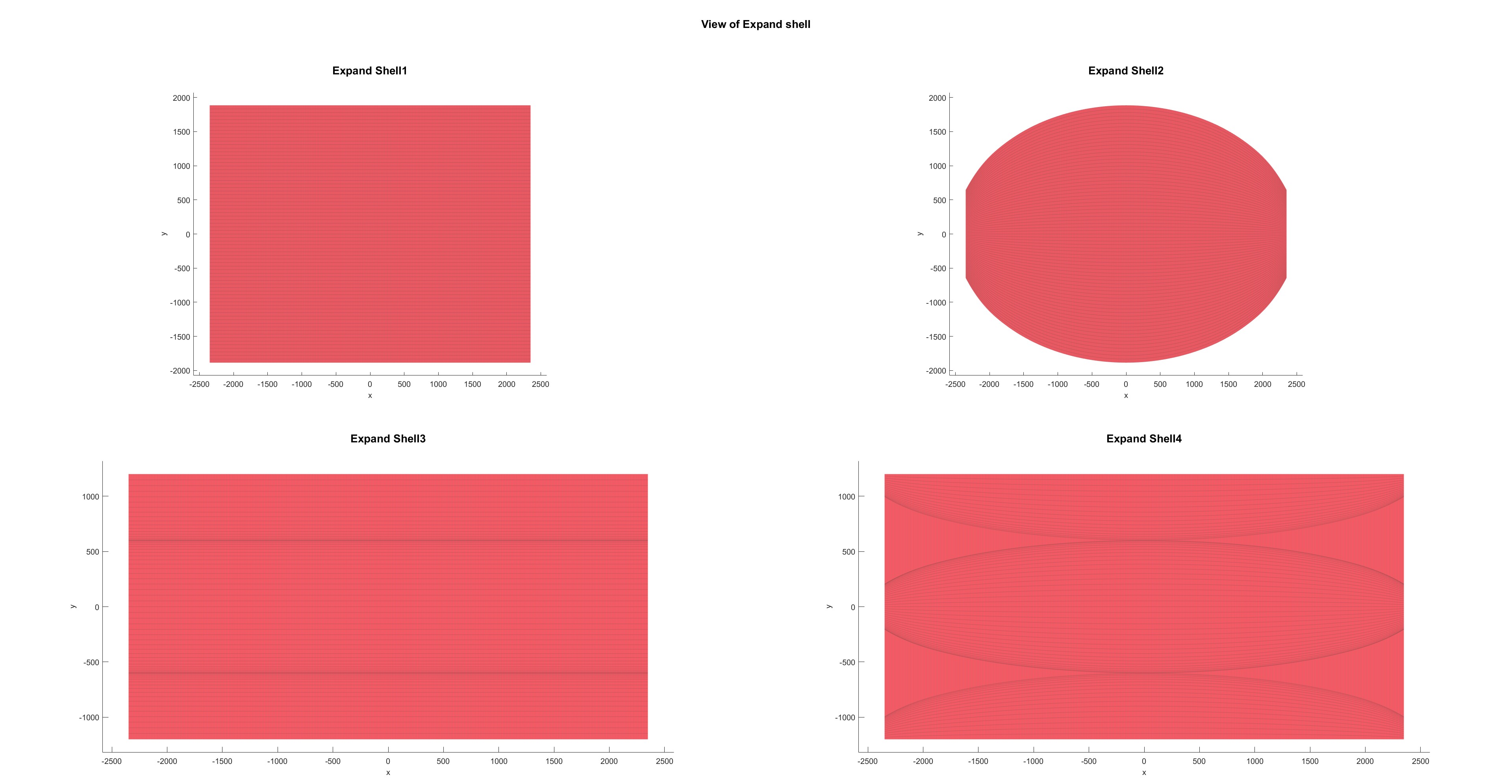
不同形状展开图:
缠绕路径:
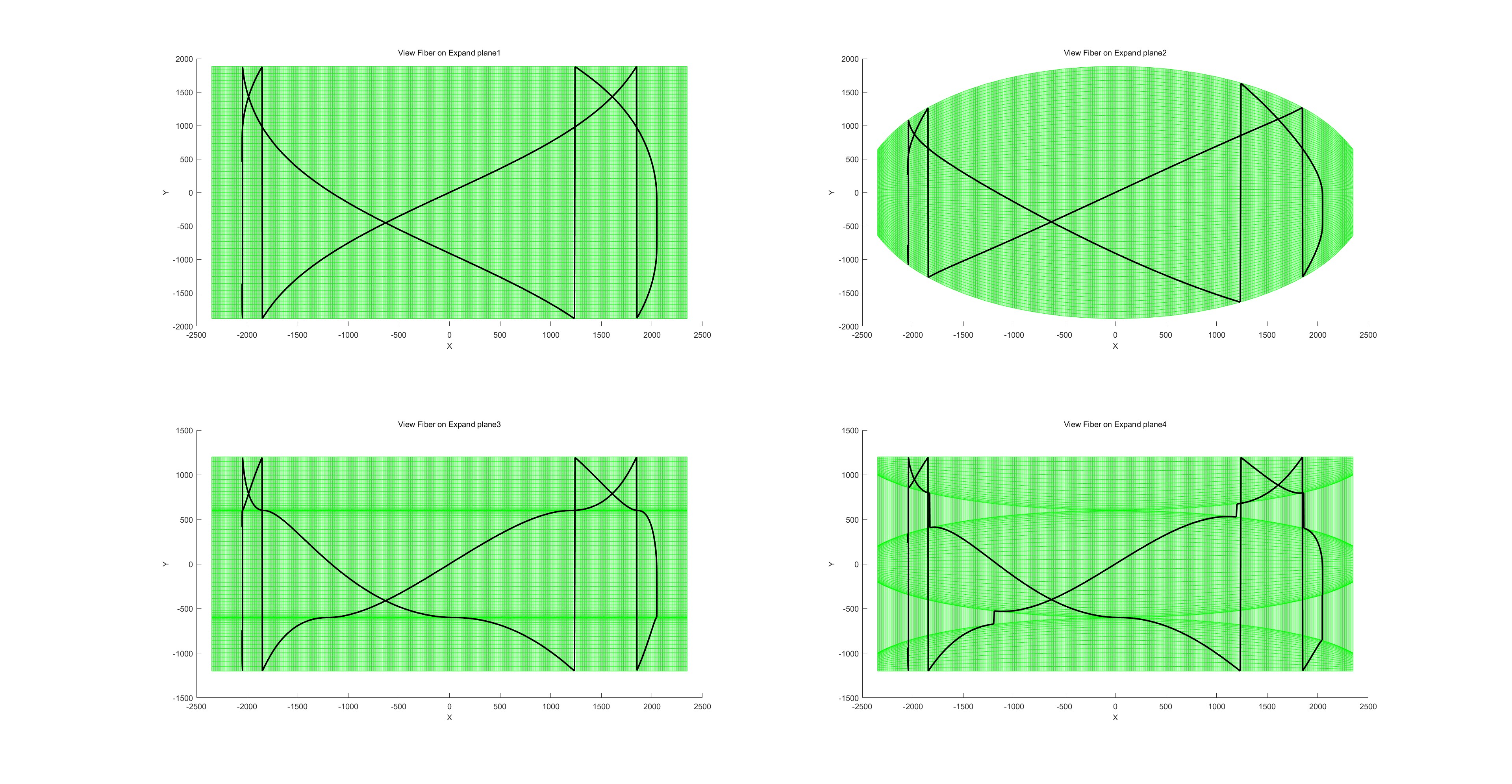
路径投影图:
缠绕完成效果图:
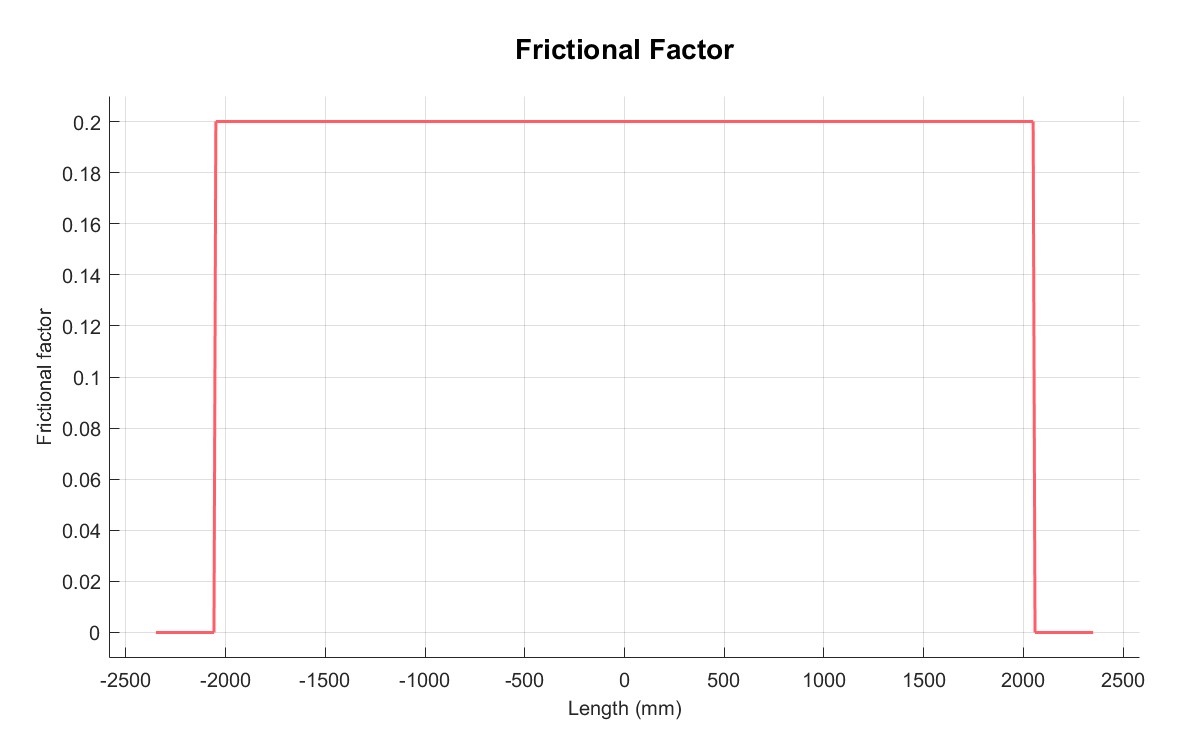 | 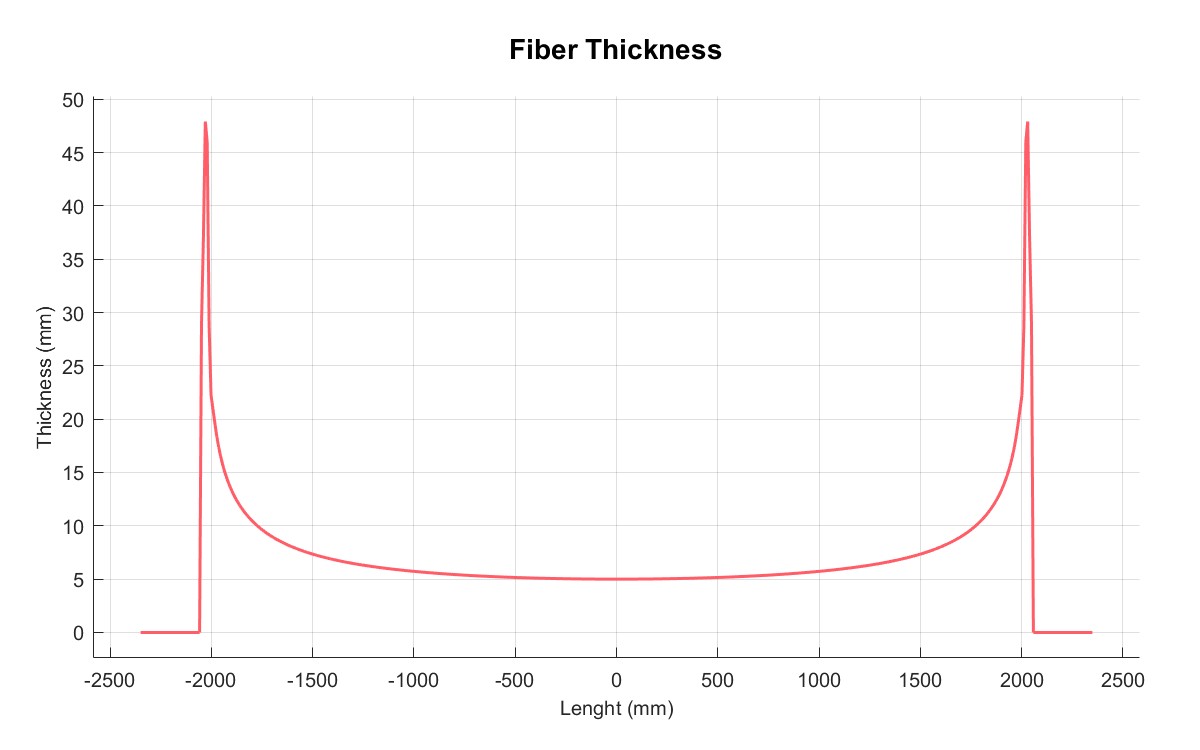 |
| 摩擦系数 | 厚度 |
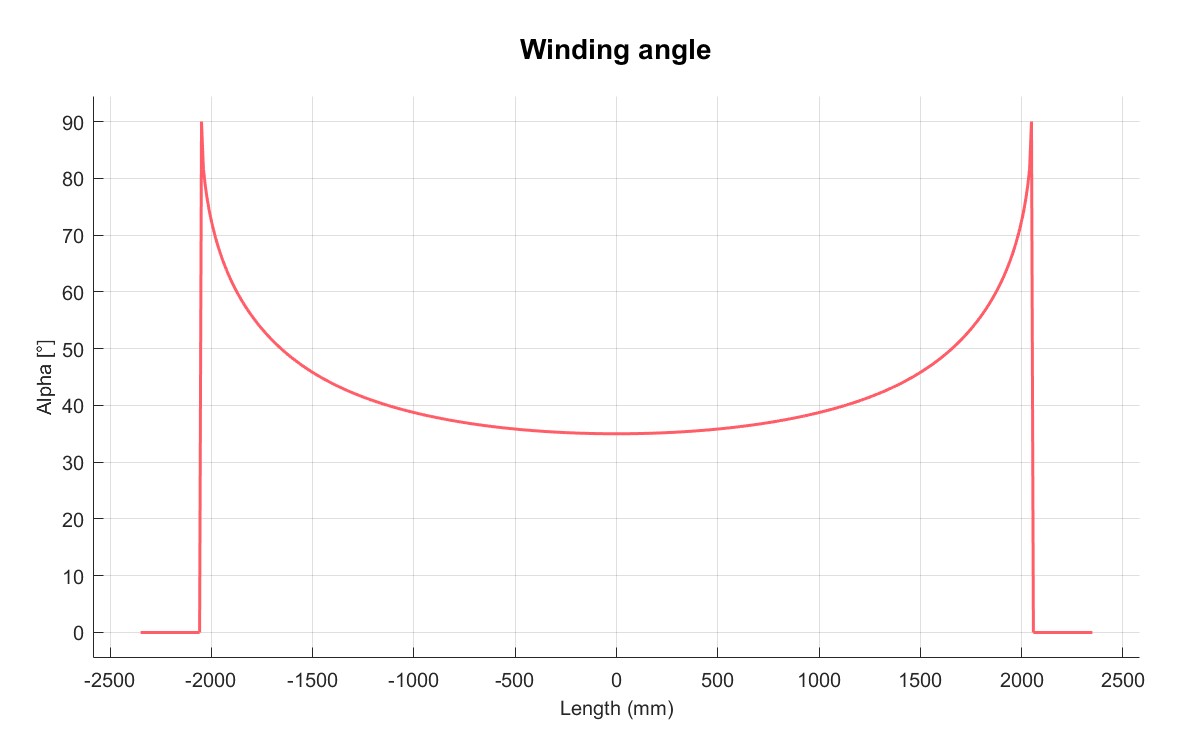 | 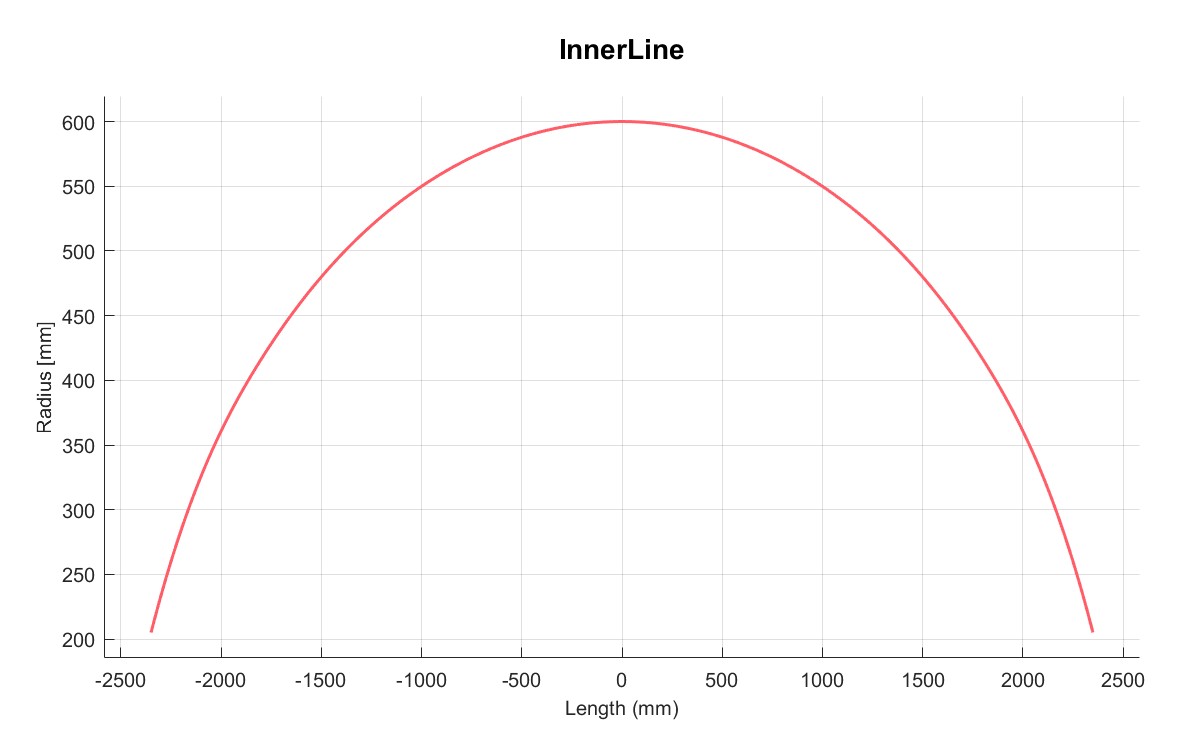 |
| 缠绕角 | 内轮廓 |
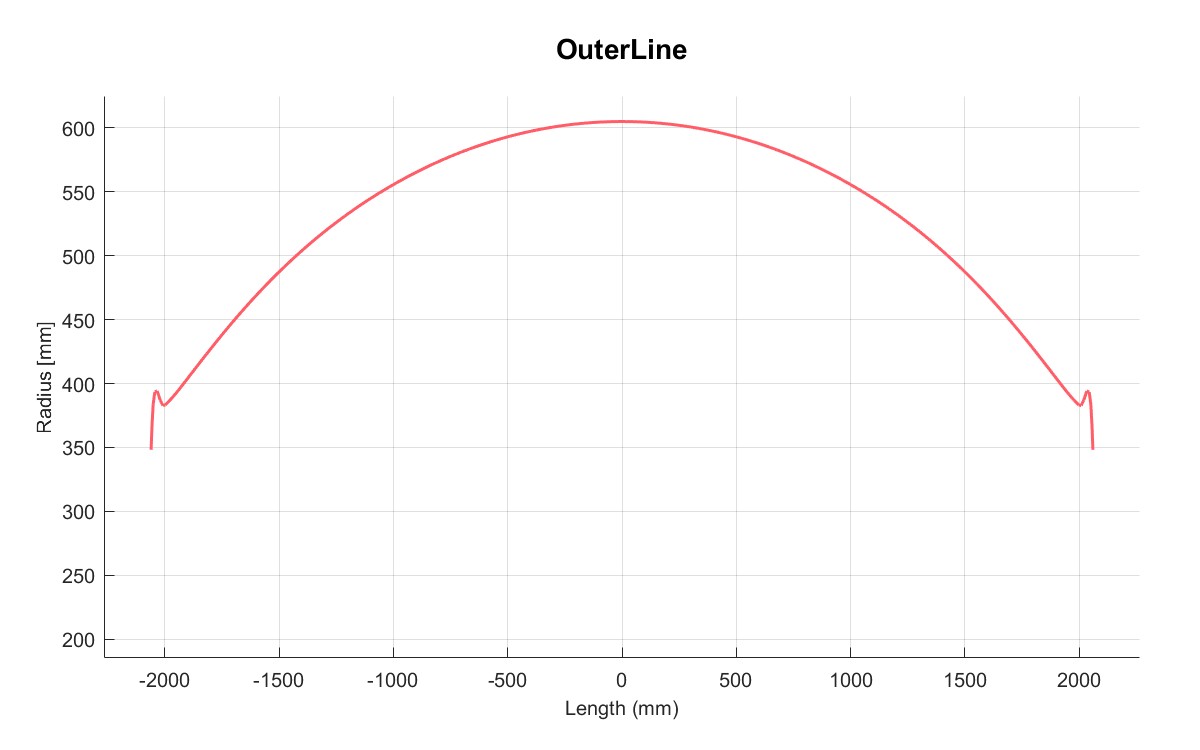 |  |
| 外部轮廓线 | 总轮廓线 |
Any curve winding (Flag=4)
a=Point2D('Point','Echo',0);
b=Line2D('Line','Echo',0);
a=AddPoint(a,-200,0);
a=AddPoint(a,[-200;100],[100;100]);
a=AddPoint(a,[100;200],[100;50]);
a=AddPoint(a,[200;250],[50;50]);
a=AddPoint(a,[250;300],[50;100]);
a=AddPoint(a,[300;350],[100;100]);
a=AddPoint(a,350,0);
b=AddCircle(b,100,a,1,'sang',160,'ang',-70,'seg',400);
b=AddLine(b,a,2);
b=AddLine(b,a,3);
b=AddLine(b,a,4);
b=AddLine(b,a,5);
b=AddLine(b,a,6);
b=AddCircle(b,100,a,7,'sang',90,'ang',-70,'seg',400);
Plot(b,'equal',1)
x=b.Point.P(:,1);
y=b.Point.P(:,2);
gap=(max(x)-min(x))/1000;
xx=min(x):gap:max(x);
yy=interp1(x,y,xx,'linear');
inputStruct1.Curve=[xx',yy'];
inputStruct1.Angle=20;
inputStruct1.Thickness=2.5;
paramsStruct1.Method=2;
paramsStruct1.Friction=[0.2,0.2];
M= solve.FilamentWinding(paramsStruct1, inputStruct1);
M= M.solve();
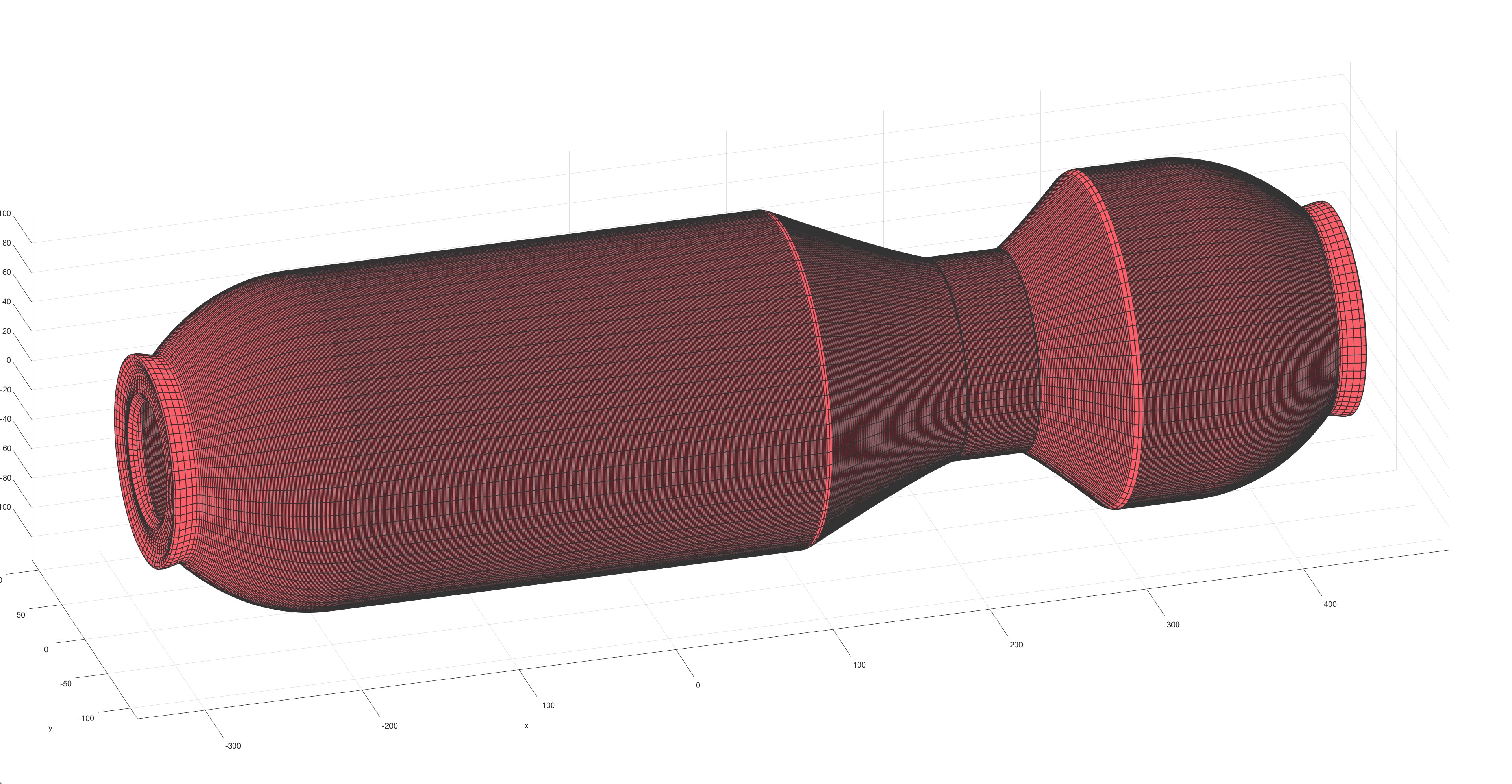
PlotShellMesh(M);
PlotExpandShell(M);
PlotPath(M);
PlotPath(M,'pattern',2);
PlotFriction(M);
PlotThickness(M);
PlotAlpha(M);
PlotInnerLine(M);
PlotOuterLine(M);
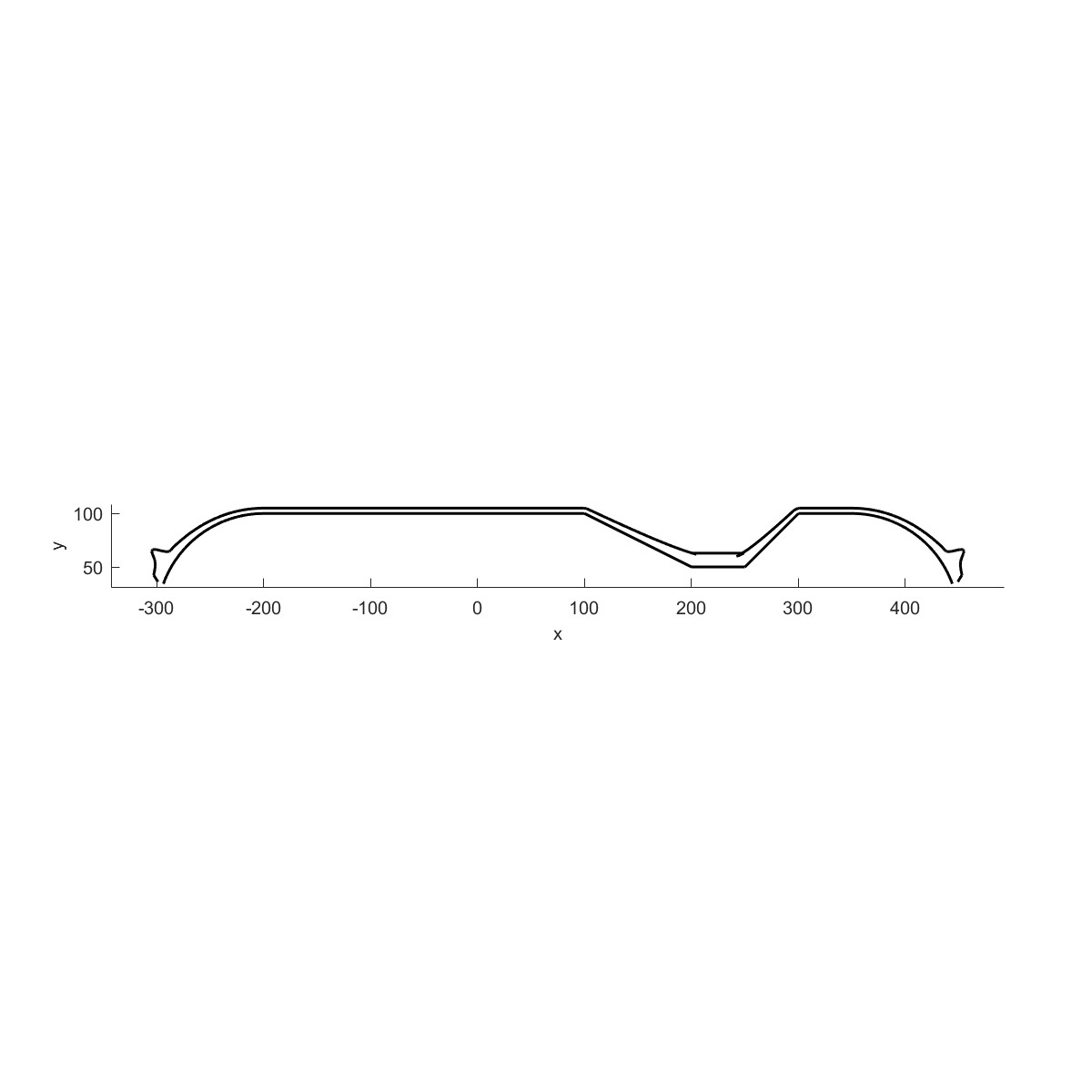
PlotShape(M);
PlotShellMesh1(M);
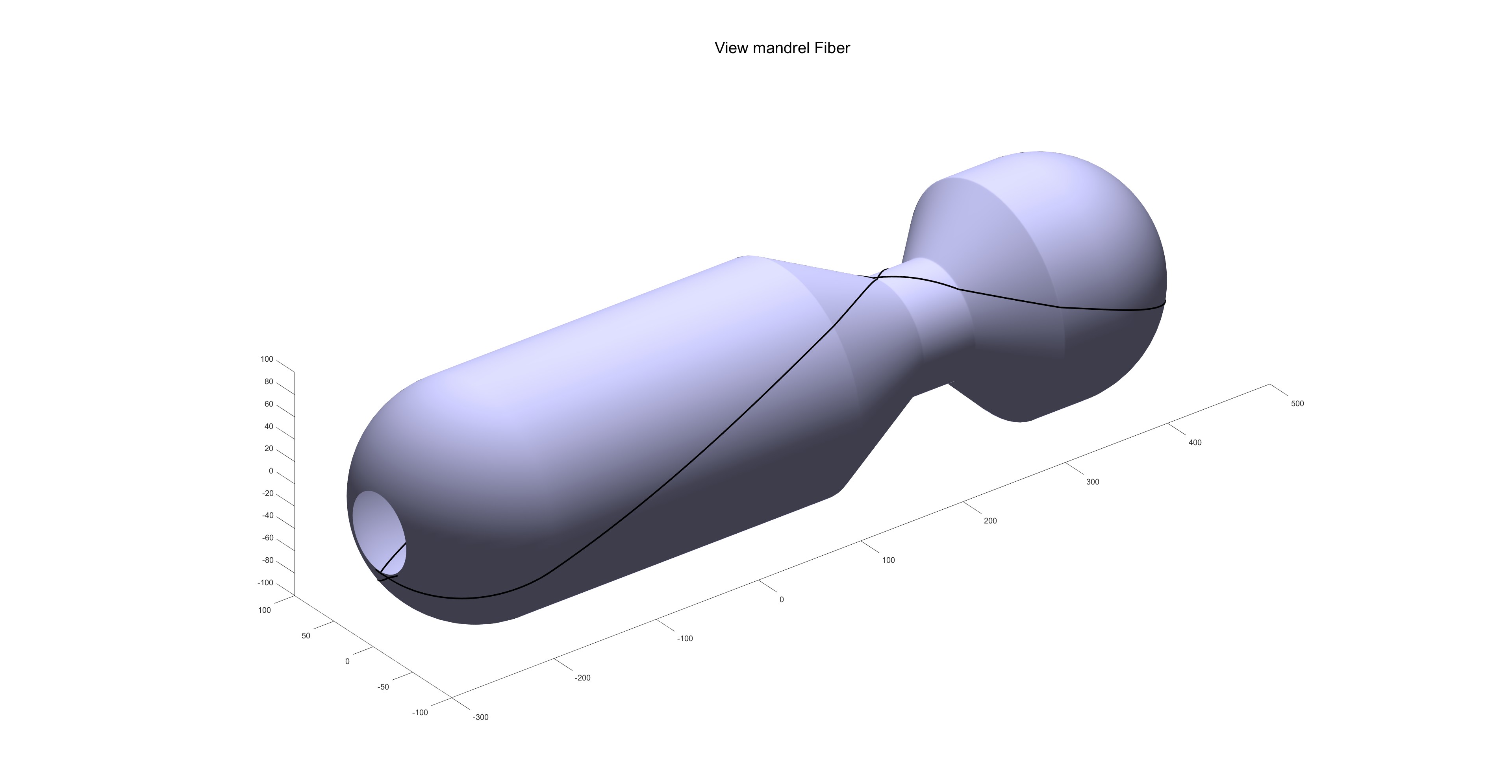
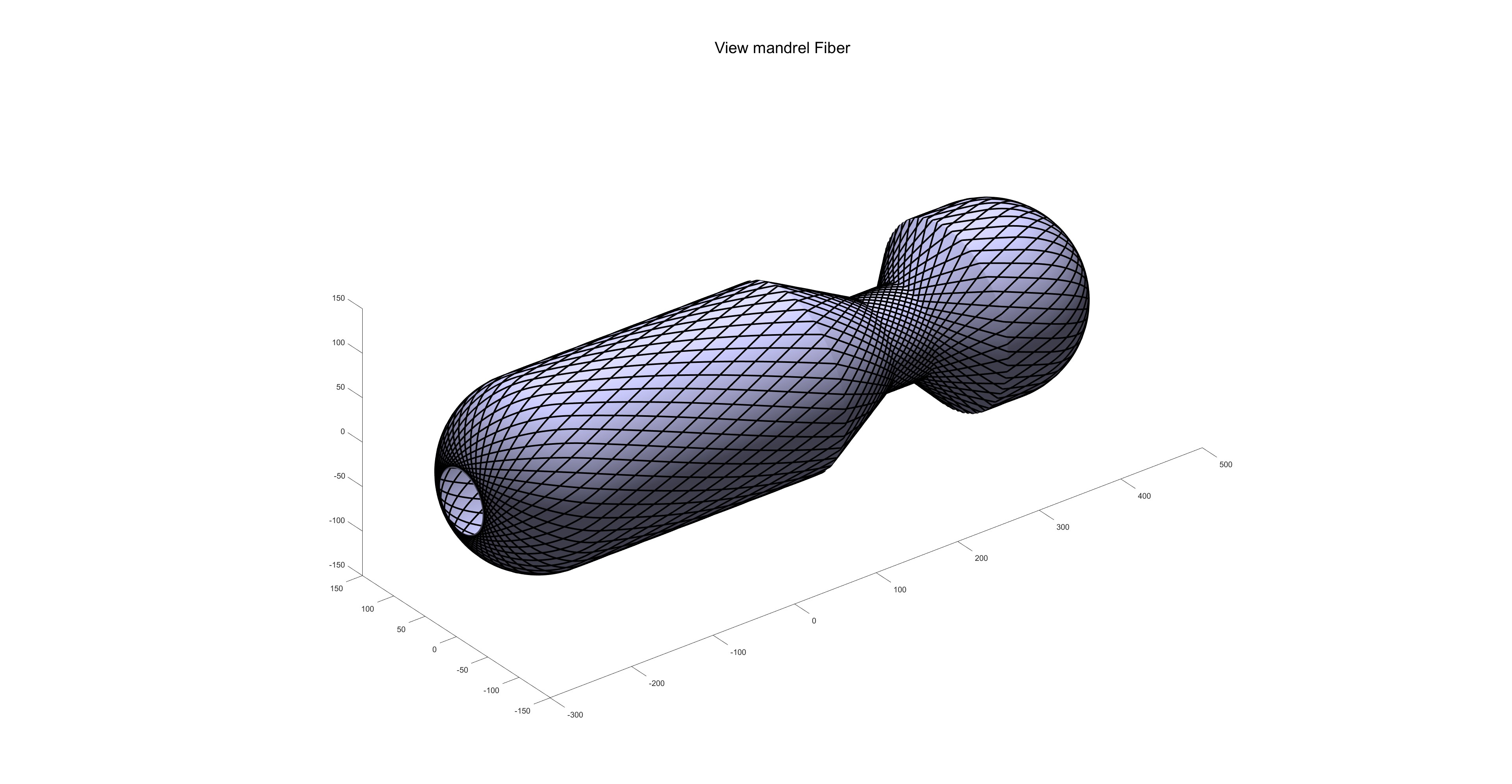
芯模形状:
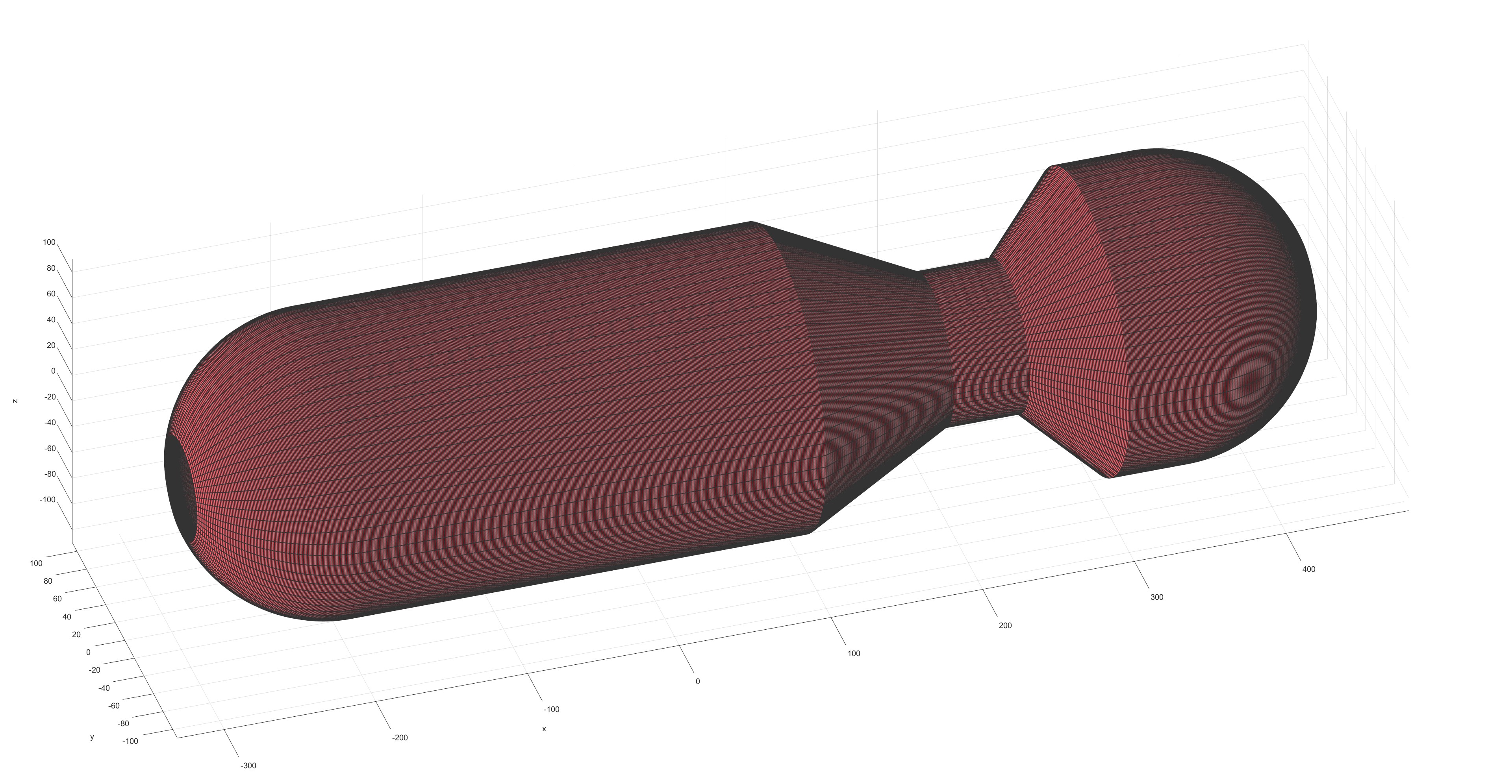
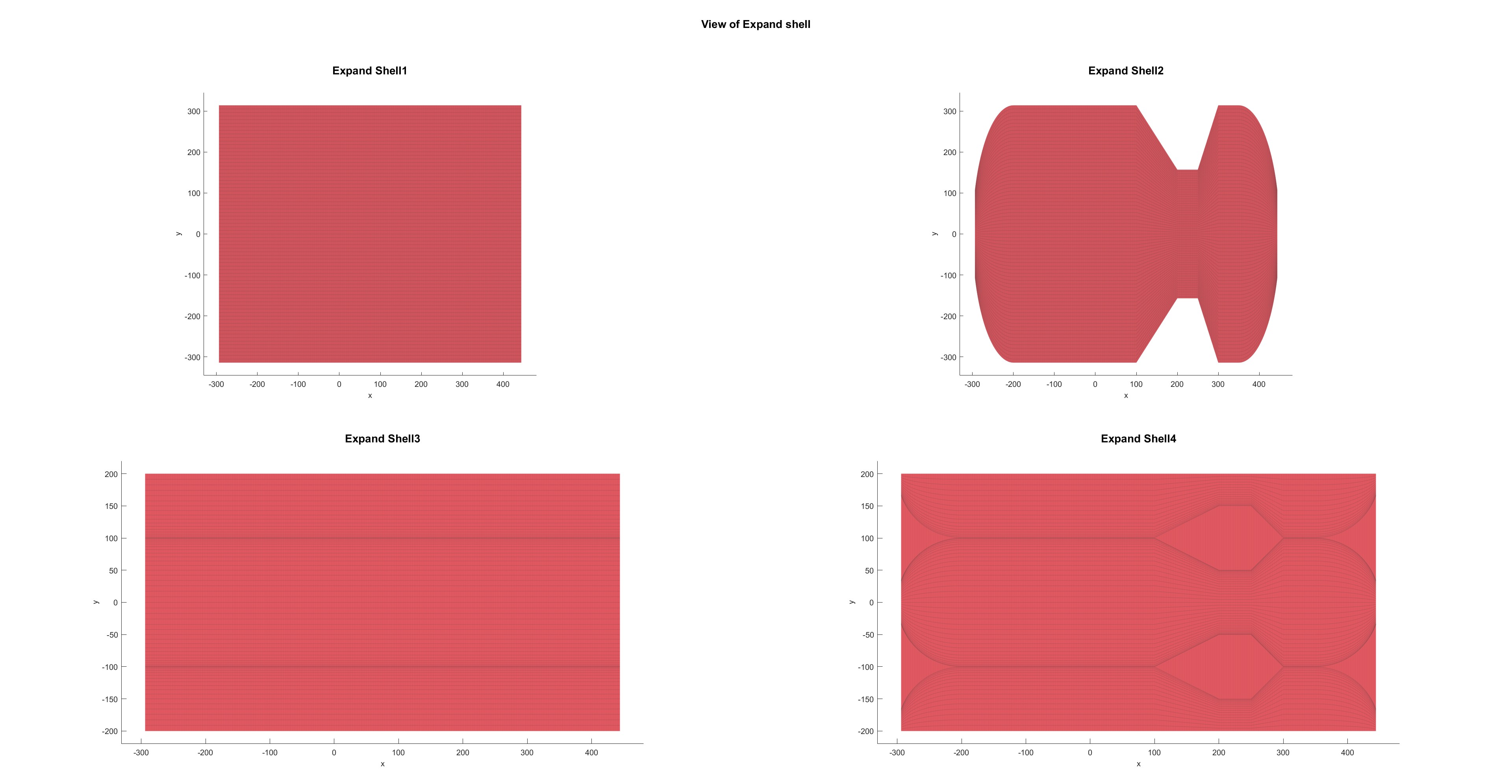
芯模展开投影图:
缠绕路径:
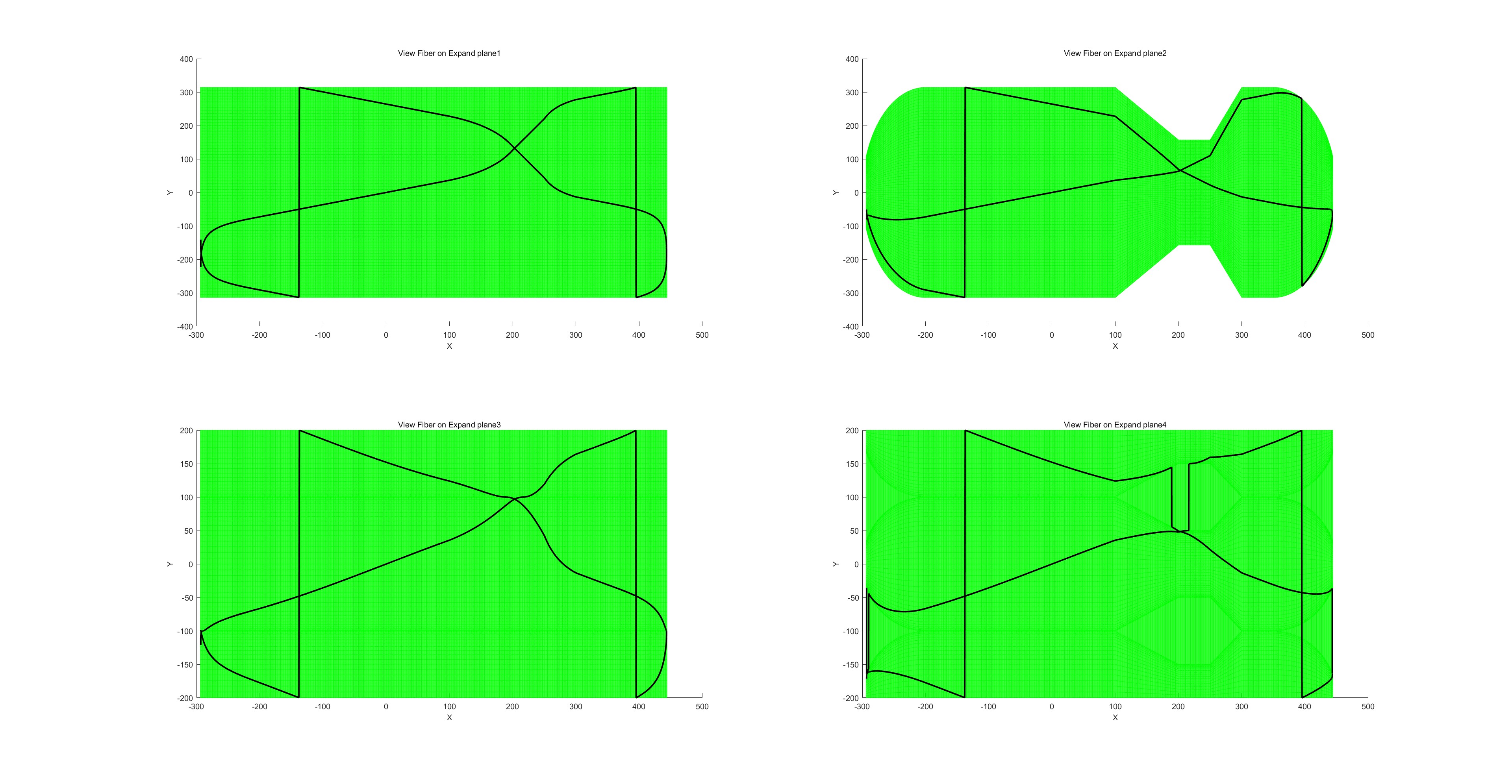
路径投影图:
缠绕线型:
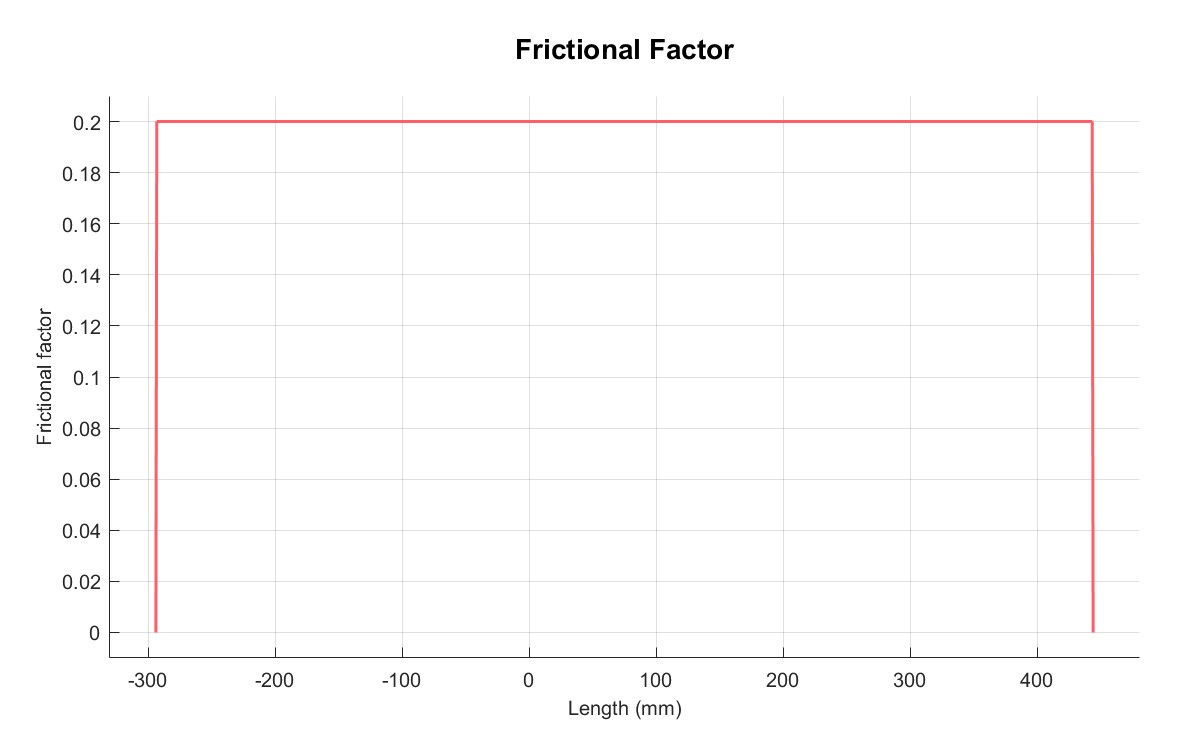 | 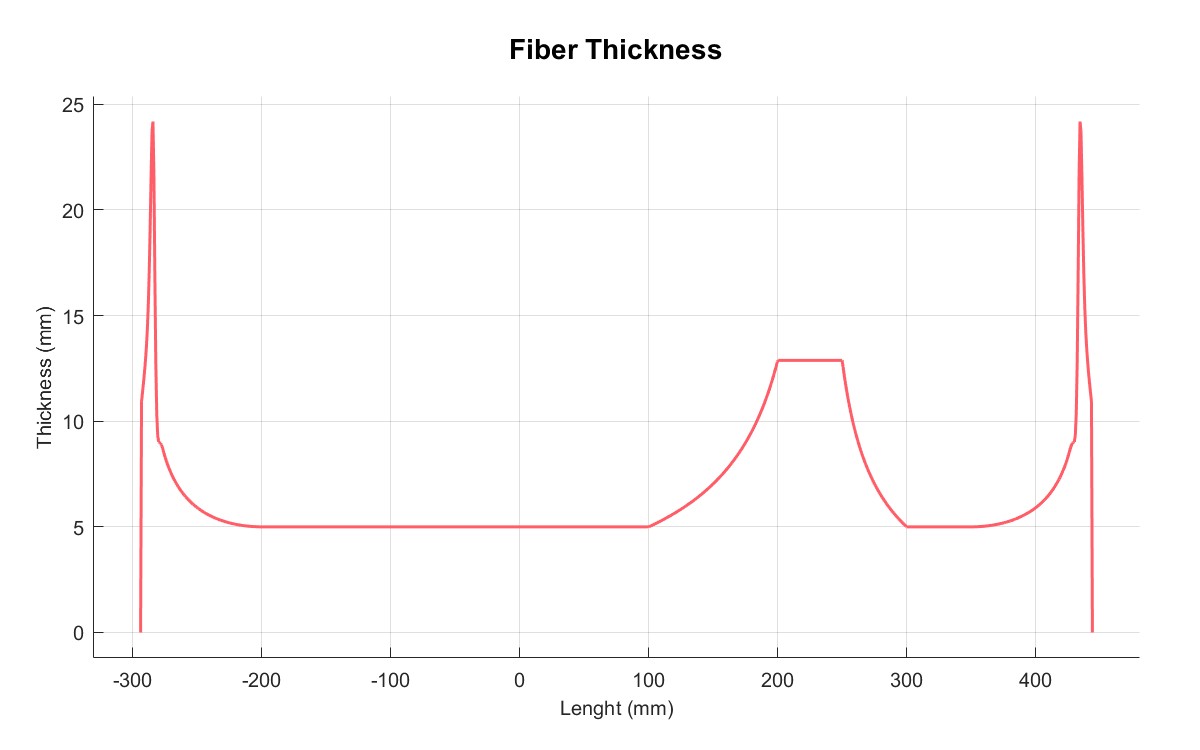 |
| 摩擦系数 | 厚度 |
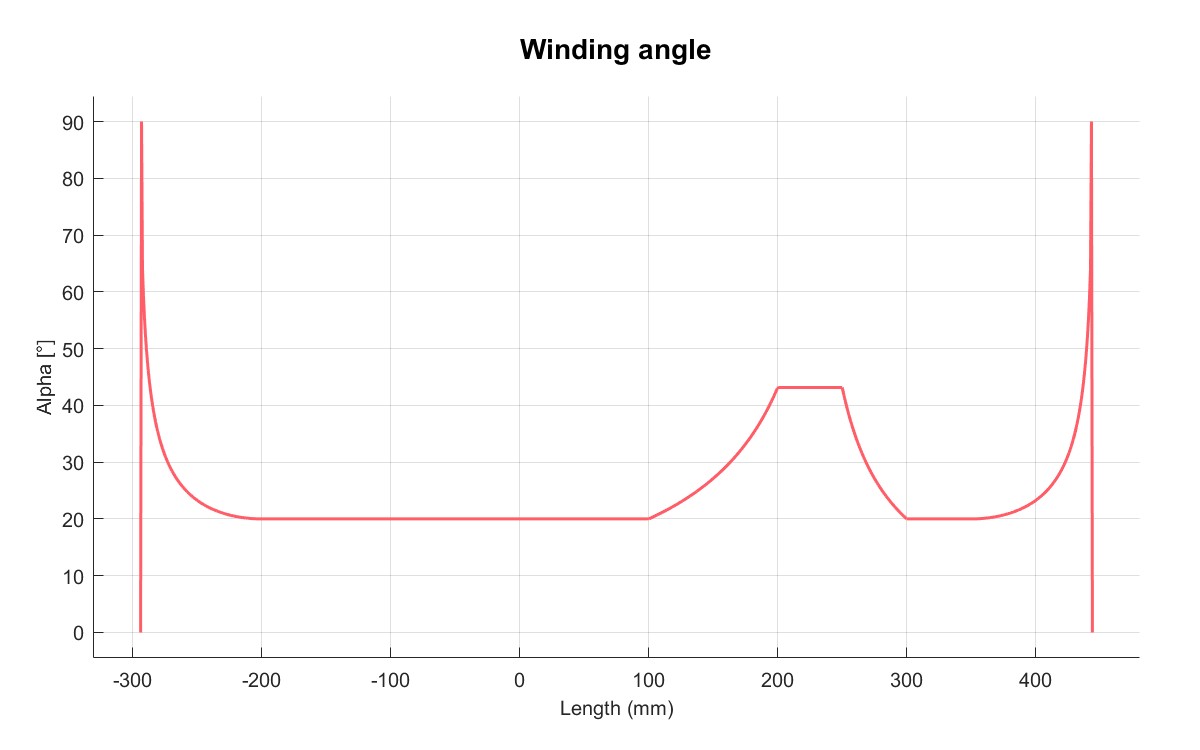 | 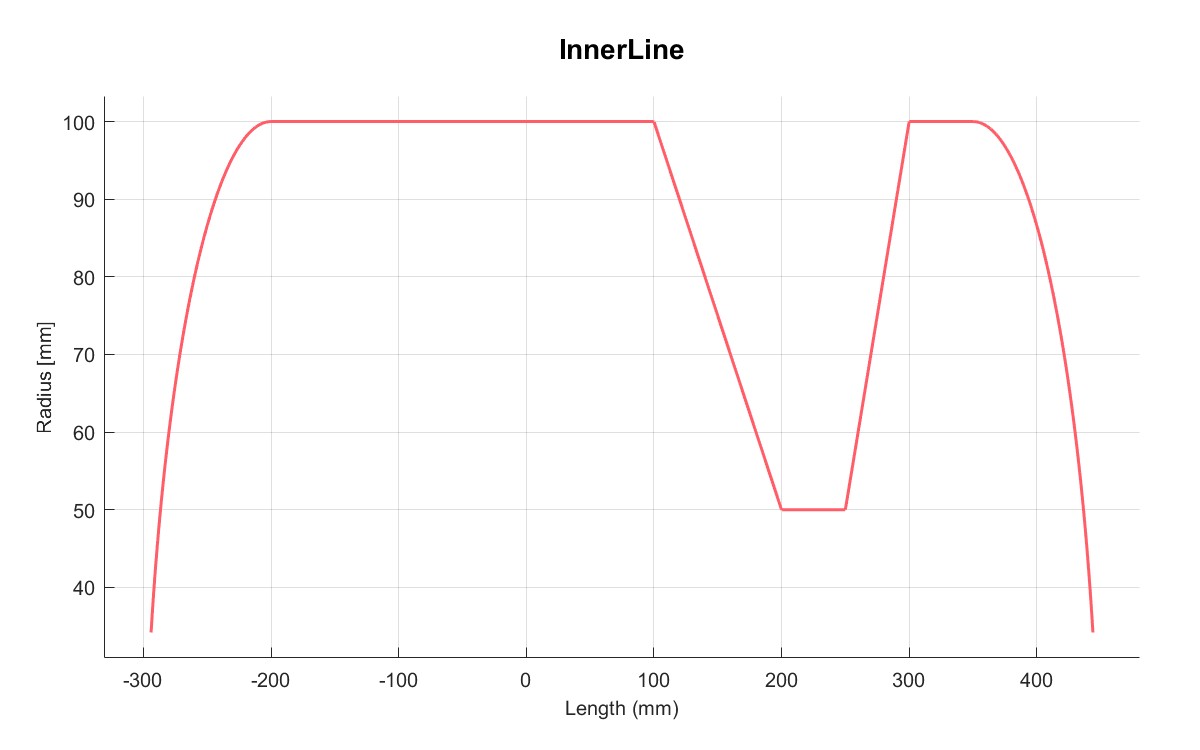 |
| 缠绕角 | 内轮廓 |
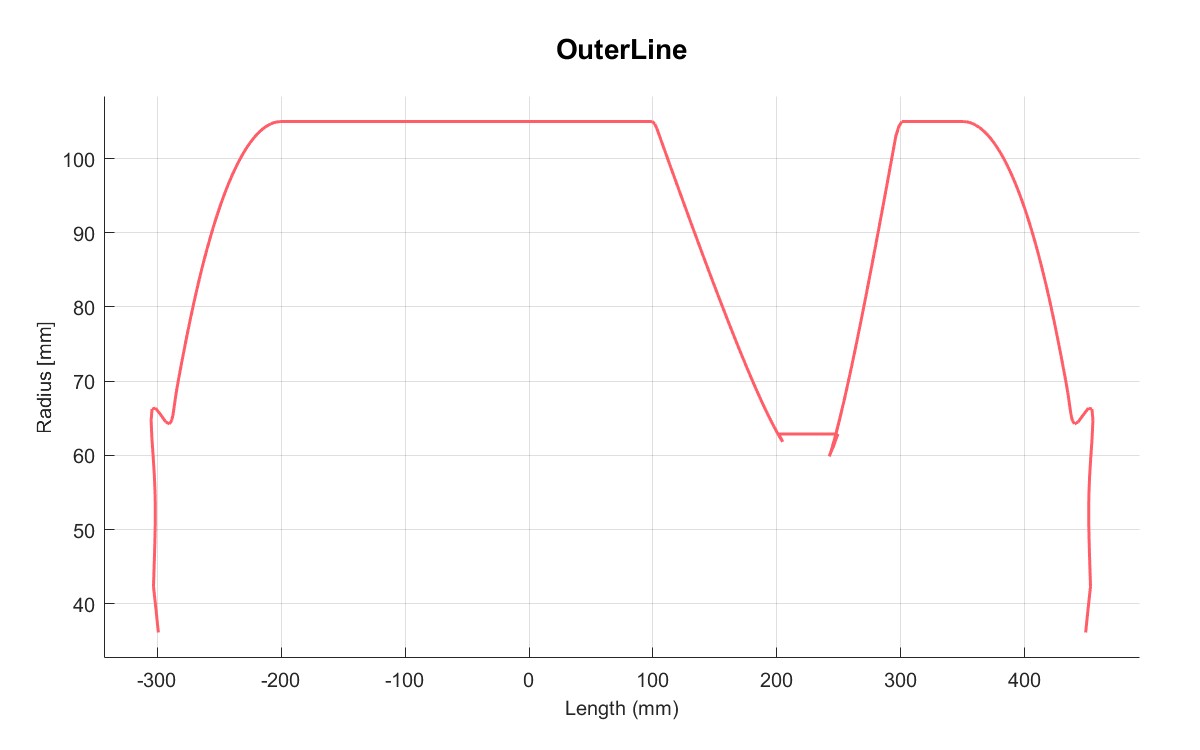 |  |
| 外部轮廓线 | 总轮廓线 |
参考文献
[1] 先进复合材料压力容器
[2] Composite filament winding
本网站基于Hexo 3-Hexz主题生成。如需转载请标注来源,如有错误请批评指正,欢迎邮件至 392176462@qq.com